Housing Market Will Improve in 2015
The lagging sector is new single family homes, where a shortage of skilled labor and buildable lots is holding back construction.

Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Today
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more delivered daily. Smart money moves start here.

Sent five days a week
Kiplinger A Step Ahead
Get practical help to make better financial decisions in your everyday life, from spending to savings on top deals.

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Closing Bell
Get today's biggest financial and investing headlines delivered to your inbox every day the U.S. stock market is open.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Adviser Intel
Financial pros across the country share best practices and fresh tactics to preserve and grow your wealth.

Delivered weekly
Kiplinger Tax Tips
Trim your federal and state tax bills with practical tax-planning and tax-cutting strategies.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Retirement Tips
Your twice-a-week guide to planning and enjoying a financially secure and richly rewarding retirement

Sent bimonthly.
Kiplinger Adviser Angle
Insights for advisers, wealth managers and other financial professionals.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Investing Weekly
Your twice-a-week roundup of promising stocks, funds, companies and industries you should consider, ones you should avoid, and why.

Sent weekly for six weeks
Kiplinger Invest for Retirement
Your step-by-step six-part series on how to invest for retirement, from devising a successful strategy to exactly which investments to choose.
Eight years after heading into the tank, the housing market is finally nearing normal. Come 2015, sales of existing homes are likely to match or top the average for 1999-2002, before home buying mania seized the U.S. A strong rental market already has the construction of multifamily dwellings back to that historical norm.
The big exception is new single-family homes. Both construction and sales of them are running at just 50% of their pre-bubble levels, and they won’t regain those norms until at least 2017. Demand is lagging for a couple of reasons: New homes tend to be more expensive than older ones, limiting the pool of buyers with the credit to buy them. And a paucity of first-time buyers means fewer owners of existing homes are able to sell and move up to a larger, more costly home.
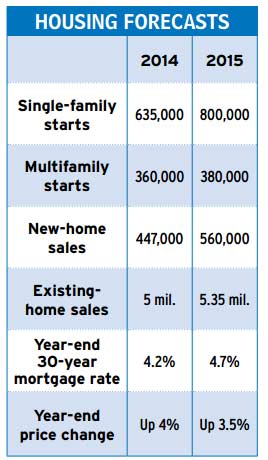
But supply is also a constraint. Builders can’t keep up even with the currently muted level of demand, according to the National Association of Home Builders.. These days, a new home typically sits on the market for just three months versus the four or five of the past. There aren’t enough skilled tradesmen: carpenters, framers and others who left the field in droves when the bubble burst. There are too few build-ready lots. It takes 15-36 months to prepare sites—building roads, water and sewer lines, bringing in electricity and so on, plus clearing regulatory hurdles. In some localities, jumping through the regulatory hoops alone can take up to seven years. Making matters worse, many lenders—gun-shy after the steep plunge in housing prices—have been loath to lend for development of raw land. So only builders with deep pockets are able to create new subdivisions. Though all these pressures are easing, it will take time for them to disappear.
From just $107.88 $24.99 for Kiplinger Personal Finance
Become a smarter, better informed investor. Subscribe from just $107.88 $24.99, plus get up to 4 Special Issues

Sign up for Kiplinger’s Free Newsletters
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and more - straight to your e-mail.
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice - straight to your e-mail.
Meanwhile, for the housing market as a whole, several positives are at work: Credit is getting easier. Half of mortgage lenders surveyed expect improved access to credit for lower prime borrowers (FICO scores of 620 to 720) over the next six months. Lenders are becoming more comfortable with the standards for loans that can be off-loaded to Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac, soothing their concerns. (Parallel rules for mortgages that can be securitized and sold will kick in next year.) So there’s more flexibility on debt-to-income ratios, and minimum down payments are sliding from 5% to 3% for Fannie- and Freddie-conforming loans, for example.
Of course, compared with the boom years, mortgages are still much harder to obtain. About half of mortgages still go to borrowers with FICO scores above 740. Though that’s better than the 60% such borrowers accounted for in 2013, it’s far more restrictive than in the early 2000s, when the average borrower score was 680. The Federal Reserve’s July 2014 Senior Loan Officer Opinion Survey on Bank Lending Practices indicated that half of mortgage loan officers considered conditions still to be tighter than average.
Also helping are higher incomes and employment; more consumers can afford purchases. In addition, there are a million more potential home buyers than usual—a backlog of young adults still living with their parents but eager to strike out on their own as soon as possible. Mortgage rates will remain modest, despite a likely slow climb over the coming year.
As for prices, we expect them to increase more slowly in 2015, now that the first pendulum swing from downturn to upturn is over and investors are seeking better returns elsewhere.
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.

David is both staff economist and reporter for The Kiplinger Letter, overseeing Kiplinger forecasts for the U.S. and world economies. Previously, he was senior principal economist in the Center for Forecasting and Modeling at IHS/GlobalInsight, and an economist in the Chief Economist's Office of the U.S. Department of Commerce. David has co-written weekly reports on economic conditions since 1992, and has forecasted GDP and its components since 1995, beating the Blue Chip Indicators forecasts two-thirds of the time. David is a Certified Business Economist as recognized by the National Association for Business Economics. He has two master's degrees and is ABD in economics from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
-
 Dow Adds 1,206 Points to Top 50,000: Stock Market Today
Dow Adds 1,206 Points to Top 50,000: Stock Market TodayThe S&P 500 and Nasdaq also had strong finishes to a volatile week, with beaten-down tech stocks outperforming.
-
 Ask the Tax Editor: Federal Income Tax Deductions
Ask the Tax Editor: Federal Income Tax DeductionsAsk the Editor In this week's Ask the Editor Q&A, Joy Taylor answers questions on federal income tax deductions
-
 States With No-Fault Car Insurance Laws (and How No-Fault Car Insurance Works)
States With No-Fault Car Insurance Laws (and How No-Fault Car Insurance Works)A breakdown of the confusing rules around no-fault car insurance in every state where it exists.
-
 Trump Reshapes Foreign Policy
Trump Reshapes Foreign PolicyThe Kiplinger Letter The President starts the new year by putting allies and adversaries on notice.
-
 Congress Set for Busy Winter
Congress Set for Busy WinterThe Kiplinger Letter The Letter editors review the bills Congress will decide on this year. The government funding bill is paramount, but other issues vie for lawmakers’ attention.
-
 The Kiplinger Letter's 10 Forecasts for 2026
The Kiplinger Letter's 10 Forecasts for 2026The Kiplinger Letter Here are some of the biggest events and trends in economics, politics and tech that will shape the new year.
-
 What to Expect from the Global Economy in 2026
What to Expect from the Global Economy in 2026The Kiplinger Letter Economic growth across the globe will be highly uneven, with some major economies accelerating while others hit the brakes.
-
 Amid Mounting Uncertainty: Five Forecasts About AI
Amid Mounting Uncertainty: Five Forecasts About AIThe Kiplinger Letter With the risk of overspending on AI data centers hotly debated, here are some forecasts about AI that we can make with some confidence.
-
 Worried About an AI Bubble? Here’s What You Need to Know
Worried About an AI Bubble? Here’s What You Need to KnowThe Kiplinger Letter Though AI is a transformative technology, it’s worth paying attention to the rising economic and financial risks. Here’s some guidance to navigate AI’s future.
-
 Will AI Videos Disrupt Social Media?
Will AI Videos Disrupt Social Media?The Kiplinger Letter With the introduction of OpenAI’s new AI social media app, Sora, the internet is about to be flooded with startling AI-generated videos.
-
 What Services Are Open During the Government Shutdown?
What Services Are Open During the Government Shutdown?The Kiplinger Letter As the shutdown drags on, many basic federal services will increasingly be affected.