Giving to Charity? Learn the Ins and Outs of Donor-Advised Funds
These simple, low-cost vehicles tend to be the most efficient and effective ways to engage in charitable giving.

Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Today
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more delivered daily. Smart money moves start here.

Sent five days a week
Kiplinger A Step Ahead
Get practical help to make better financial decisions in your everyday life, from spending to savings on top deals.

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Closing Bell
Get today's biggest financial and investing headlines delivered to your inbox every day the U.S. stock market is open.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Adviser Intel
Financial pros across the country share best practices and fresh tactics to preserve and grow your wealth.

Delivered weekly
Kiplinger Tax Tips
Trim your federal and state tax bills with practical tax-planning and tax-cutting strategies.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Retirement Tips
Your twice-a-week guide to planning and enjoying a financially secure and richly rewarding retirement

Sent bimonthly.
Kiplinger Adviser Angle
Insights for advisers, wealth managers and other financial professionals.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Investing Weekly
Your twice-a-week roundup of promising stocks, funds, companies and industries you should consider, ones you should avoid, and why.

Sent weekly for six weeks
Kiplinger Invest for Retirement
Your step-by-step six-part series on how to invest for retirement, from devising a successful strategy to exactly which investments to choose.
According to the National Philanthropic Trust, Americans gave $358.38 billion to charities in 2014, a 7.1% uptick from the previous year. And with the deadline for deducting charitable contributions approaching on Dec. 31, now is a good time to give back to an organization and/or support a current relief effort.
While there are multiple vehicles available to help support philanthropic giving, we find that donor-advised funds (DAF) tend to be the most efficient and effective giving vehicles. They are simple, low cost, and flexible. They allow donors to maximize the tax benefits of charitable giving while supporting their favorite organizations.
What is a Donor-Advised Fund?
From just $107.88 $24.99 for Kiplinger Personal Finance
Become a smarter, better informed investor. Subscribe from just $107.88 $24.99, plus get up to 4 Special Issues

Sign up for Kiplinger’s Free Newsletters
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and more - straight to your e-mail.
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice - straight to your e-mail.
A DAF is simply an account that helps givers manage their charitable contributions. Through an agreement with a DAF provider, a donor creates a specially named account (i.e. “Smith Family Fund”) to which irrevocable contributions are made. The donor receives an immediate tax deduction but is not forced to make any grants. They can work with their adviser to invest and grow the assets and recommend grants to their favorite non-profit, 501(c)(3) organizations at their leisure.
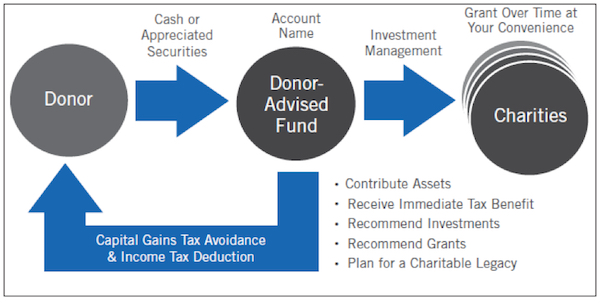
Why Use a Donor-Advised Fund?
Simplicity. Unlike a private foundation, the donor is not responsible for hiring attorneys and accountants or maintaining a board of directors. The sponsoring organization that holds the fund takes responsibility of all the expensive administration work, including filing annual returns and preparing financial statements.
Tax Efficiency. DAF contributions provide a federal income tax deduction up to 50 percent of adjusted gross income for cash contributions and up to 30 percent of adjusted gross income for appreciated securities. Along with publicly traded securities, DAF holders can also contribute complex assets such as real estate, limited partnership interests, private C- and S-Corp stock, and other privately held assets.
Flexibility. DAF holders receive an immediate tax deduction for their contribution but they are not subject to a legal minimum payout requirement like a private foundation. The flexibility helps donors maximize tax benefits while helping them be more systematic and methodical about their giving.
If you haven’t engaged in charitable giving yet, now is a great time to start. And in doing so, consider the benefits of a DAF—to you and to the future recipients.
Taylor Schulte, CFP® is founder and CEO of Define Financial, a San Diego-based fee-only firm. He is passionate about helping clients accumulate wealth and plan for retirement.
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.

Taylor Schulte, CFP®, is founder and CEO of Define Financial, a fee-only wealth management firm in San Diego. In addition, Schulte hosts The Stay Wealthy Retirement Podcast, teaching people how to reduce taxes, invest smarter, and make work optional. He has been recognized as a top 40 Under 40 adviser by InvestmentNews and one of the top 100 most influential advisers by Investopedia.
-
 Here’s How to Stream the Super Bowl for Less
Here’s How to Stream the Super Bowl for LessWe'll show you the least expensive ways to stream football's biggest event.
-
 The Cost of Leaving Your Money in a Low-Rate Account
The Cost of Leaving Your Money in a Low-Rate AccountWhy parking your cash in low-yield accounts could be costing you, and smarter alternatives that preserve liquidity while boosting returns.
-
 I want to sell our beach house to retire now, but my wife wants to keep it.
I want to sell our beach house to retire now, but my wife wants to keep it.I want to sell the $610K vacation home and retire now, but my wife envisions a beach retirement in 8 years. We asked financial advisers to weigh in.
-
 How to Add a Pet Trust to Your Estate Plan: Don't Leave Your Best Friend to Chance
How to Add a Pet Trust to Your Estate Plan: Don't Leave Your Best Friend to ChanceAdding a pet trust to your estate plan can ensure your pets are properly looked after when you're no longer able to care for them. This is how to go about it.
-
 Want to Avoid Leaving Chaos in Your Wake? Don't Leave Behind an Outdated Estate Plan
Want to Avoid Leaving Chaos in Your Wake? Don't Leave Behind an Outdated Estate PlanAn outdated or incomplete estate plan could cause confusion for those handling your affairs at a difficult time. This guide highlights what to update and when.
-
 I'm a Financial Adviser: This Is Why I Became an Advocate for Fee-Only Financial Advice
I'm a Financial Adviser: This Is Why I Became an Advocate for Fee-Only Financial AdviceCan financial advisers who earn commissions on product sales give clients the best advice? For one professional, changing track was the clear choice.
-
 I Met With 100-Plus Advisers to Develop This Road Map for Adopting AI
I Met With 100-Plus Advisers to Develop This Road Map for Adopting AIFor financial advisers eager to embrace AI but unsure where to start, this road map will help you integrate the right tools and safeguards into your work.
-
 The Referral Revolution: How to Grow Your Business With Trust
The Referral Revolution: How to Grow Your Business With TrustYou can attract ideal clients by focusing on value and leveraging your current relationships to create a referral-based practice.
-
 This Is How You Can Land a Job You'll Love
This Is How You Can Land a Job You'll Love"Work How You Are Wired" leads job seekers on a journey of self-discovery that could help them snag the job of their dreams.
-
 65 or Older? Cut Your Tax Bill Before the Clock Runs Out
65 or Older? Cut Your Tax Bill Before the Clock Runs OutThanks to the OBBBA, you may be able to trim your tax bill by as much as $14,000. But you'll need to act soon, as not all of the provisions are permanent.
-
 The Key to a Successful Transition When Selling Your Business: Start the Process Sooner Than You Think You Need To
The Key to a Successful Transition When Selling Your Business: Start the Process Sooner Than You Think You Need ToWay before selling your business, you can align tax strategy, estate planning, family priorities and investment decisions to create flexibility.