A Watched Portfolio Never Performs
The more you agonize over your investment portfolio, the worse you think it's performing ... even when it's doing really well.


Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Today
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more delivered daily. Smart money moves start here.

Sent five days a week
Kiplinger A Step Ahead
Get practical help to make better financial decisions in your everyday life, from spending to savings on top deals.

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Closing Bell
Get today's biggest financial and investing headlines delivered to your inbox every day the U.S. stock market is open.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Adviser Intel
Financial pros across the country share best practices and fresh tactics to preserve and grow your wealth.

Delivered weekly
Kiplinger Tax Tips
Trim your federal and state tax bills with practical tax-planning and tax-cutting strategies.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Retirement Tips
Your twice-a-week guide to planning and enjoying a financially secure and richly rewarding retirement

Sent bimonthly.
Kiplinger Adviser Angle
Insights for advisers, wealth managers and other financial professionals.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Investing Weekly
Your twice-a-week roundup of promising stocks, funds, companies and industries you should consider, ones you should avoid, and why.

Sent weekly for six weeks
Kiplinger Invest for Retirement
Your step-by-step six-part series on how to invest for retirement, from devising a successful strategy to exactly which investments to choose.
Perception is reality when it comes to a portfolio.
Many investors feel like their portfolios are always underperforming. No matter how well diversified or how many best-in-class strategies they own, it rarely feels like they're making progress.
The reason it feels this way is the same reason a watched pot never boils: the observer effect. By simply looking at our portfolios, we are affecting our performance.
From just $107.88 $24.99 for Kiplinger Personal Finance
Become a smarter, better informed investor. Subscribe from just $107.88 $24.99, plus get up to 4 Special Issues

Sign up for Kiplinger’s Free Newsletters
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and more - straight to your e-mail.
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice - straight to your e-mail.
We are all aware of how making emotional decisions can destroy portfolio returns. But few are aware that how we mentally perceive performance can affect how we make investment decisions — even more so than the cold, hard facts.
Effects of prospect theory
The gap between performance and perceived performance is explained by prospect theory. Investopedia describes prospect theory as a phenomenon where “… losses cause greater emotional impact on an individual than does an equivalent amount of gain…”
This might be because fear is an absolute emotion and greed is a relative one. Fear is essential to our survival instincts and thus, we are inclined to draw out negativity to its worst conclusion. In the inverse, we expect good things to happen so we discount positivity. Even when things are the best and we’re comfortably in pursuit of greed, we are relatively certain that at any moment the other shoe is about to drop.
Whatever the explanation, this influence on investors’ psyches and their subsequent behavior can have a devastating impact on investment results.
The emotional experience of investing
The chart below shows how our perceptions, or misconceptions, can distort reality and create pain.
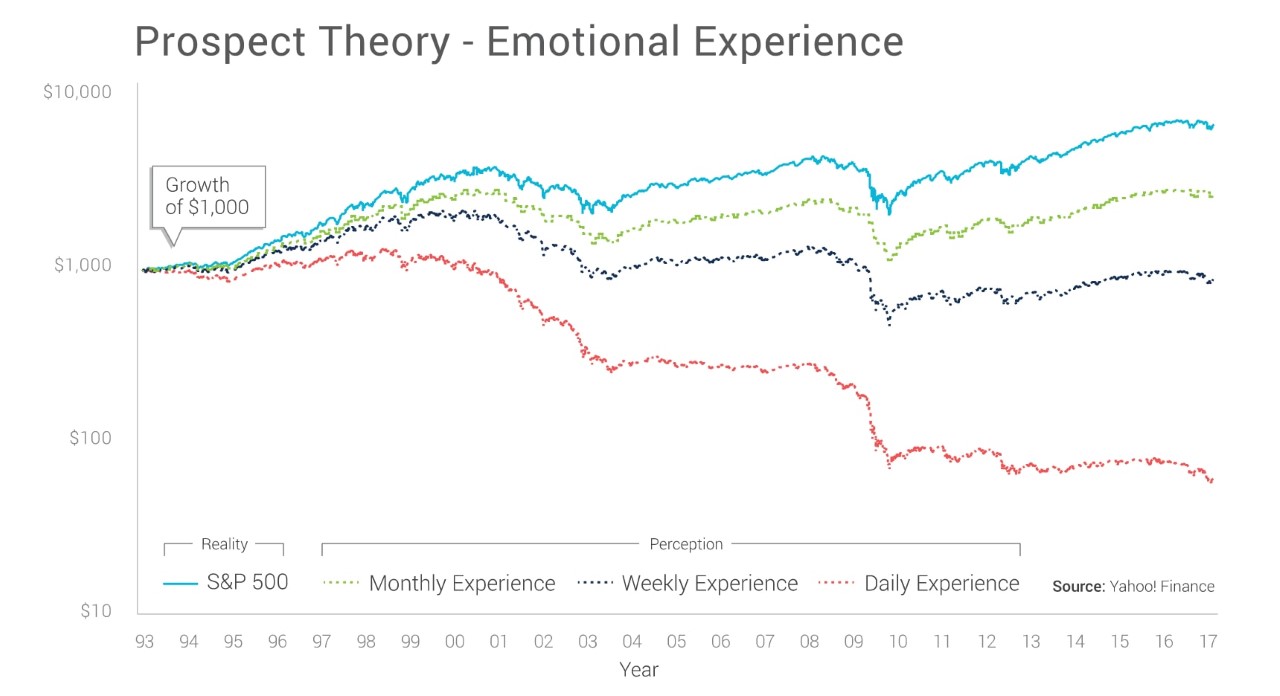
It depicts a simple example of how an investor might experience prospect theory: The raw performance of the S&P 500 index is in solid blue. However, since each person’s emotional experience changes depending on how often they observe this performance, we demonstrate the likely emotional experience in the dotted lines.
The green dotted line is how an investor, according to prospect theory, will perceive the portfolio if they look at it monthly. The dark blue dotted line is if they look at it weekly. The red dotted line is if they look at it daily.
In reality, the S&P 500 appreciated by over 700% during this time period. Investors who checked their investment results just one time, after 23 years, would see this very large gain. Plus they would not have experienced any of the volatility (and corresponding fear or greed) along the way. In other words, these investors avoided the negative effects of prospect theory.
On the other hand, investors who viewed their investment results monthly, according to the theory, would have a very different emotional experience. Remember, the theory suggests that a 10% gain feels moderately good, while a 10% loss feels exceptionally bad. At a monthly frequency, over 23 years, that’s 276 opportunities for prospect theory to create negative emotions.
The impact gets much worse the more frequent the observations. This leads to a dangerous cycle between fear, greed and prospect theory: When things are good, performance is discounted, and when they’re bad, investors overreact. This skewed perception enhances fear or greed, leading to more emotional decision-making that seems to never pay off. Why? Because the good is never good enough and the bad feels worse than it actually is. And the cycle continues.
Cure the negative feedback cycle
Now, we know investors aren’t going to just ignore their portfolios. They might get notifications from CNBC and Bloomberg on favorite stocks. Major social, economic or political movements around the globe will still send investors rushing to check the effect on their portfolios.
But at least investors can be conscious of the enemy — their own emotions.
Despite the influx of information, there’s still an easy way to counter prospect theory: portfolio balance. The more balanced a portfolio is, the less volatility it’ll experience. Lower drawdowns mean less fear and greed, which of course means fewer emotional decisions and reduced effects of prospect theory. Awareness of this pattern helps, too.
Finding balance in today’s economy
Being aware of the benefits of true diversification and the damage that fear and greed can do is as crucial as keeping up with the financial news. Being aware of the games that prospect theory can play with the mind is nearly as important as choosing quality investments, at least if investors are seeking to achieve a balanced portfolio that helps them feel in control of their financial futures.
Otherwise, even when they’re making money, they’ll never feel like they’re keeping up with the Joneses.
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.

Stephen Scott is an alternatives and hedge fund investment veteran, with more than 25 years of experience in due diligence, risk management and index construction.
-
 How Much It Costs to Host a Super Bowl Party in 2026
How Much It Costs to Host a Super Bowl Party in 2026Hosting a Super Bowl party in 2026 could cost you. Here's a breakdown of food, drink and entertainment costs — plus ways to save.
-
 3 Reasons to Use a 5-Year CD As You Approach Retirement
3 Reasons to Use a 5-Year CD As You Approach RetirementA five-year CD can help you reach other milestones as you approach retirement.
-
 Your Adult Kids Are Doing Fine. Is It Time To Spend Some of Their Inheritance?
Your Adult Kids Are Doing Fine. Is It Time To Spend Some of Their Inheritance?If your kids are successful, do they need an inheritance? Ask yourself these four questions before passing down another dollar.
-
 The 4 Estate Planning Documents Every High-Net-Worth Family Needs (Not Just a Will)
The 4 Estate Planning Documents Every High-Net-Worth Family Needs (Not Just a Will)The key to successful estate planning for HNW families isn't just drafting these four documents, but ensuring they're current and immediately accessible.
-
 Love and Legacy: What Couples Rarely Talk About (But Should)
Love and Legacy: What Couples Rarely Talk About (But Should)Couples who talk openly about finances, including estate planning, are more likely to head into retirement joyfully. How can you get the conversation going?
-
 How to Get the Fair Value for Your Shares When You Are in the Minority Vote on a Sale of Substantially All Corporate Assets
How to Get the Fair Value for Your Shares When You Are in the Minority Vote on a Sale of Substantially All Corporate AssetsWhen a sale of substantially all corporate assets is approved by majority vote, shareholders on the losing side of the vote should understand their rights.
-
 How to Add a Pet Trust to Your Estate Plan: Don't Leave Your Best Friend to Chance
How to Add a Pet Trust to Your Estate Plan: Don't Leave Your Best Friend to ChanceAdding a pet trust to your estate plan can ensure your pets are properly looked after when you're no longer able to care for them. This is how to go about it.
-
 Want to Avoid Leaving Chaos in Your Wake? Don't Leave Behind an Outdated Estate Plan
Want to Avoid Leaving Chaos in Your Wake? Don't Leave Behind an Outdated Estate PlanAn outdated or incomplete estate plan could cause confusion for those handling your affairs at a difficult time. This guide highlights what to update and when.
-
 I'm a Financial Adviser: This Is Why I Became an Advocate for Fee-Only Financial Advice
I'm a Financial Adviser: This Is Why I Became an Advocate for Fee-Only Financial AdviceCan financial advisers who earn commissions on product sales give clients the best advice? For one professional, changing track was the clear choice.
-
 I Met With 100-Plus Advisers to Develop This Road Map for Adopting AI
I Met With 100-Plus Advisers to Develop This Road Map for Adopting AIFor financial advisers eager to embrace AI but unsure where to start, this road map will help you integrate the right tools and safeguards into your work.
-
 The Referral Revolution: How to Grow Your Business With Trust
The Referral Revolution: How to Grow Your Business With TrustYou can attract ideal clients by focusing on value and leveraging your current relationships to create a referral-based practice.