Age Targets: How Much Should You Have Saved for Retirement By Now?
Retirement savings benchmarks can be helpful tools to prompt action ... IF they're realistic. See if your savings are at least in the right ballpark.


Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Today
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more delivered daily. Smart money moves start here.

Sent five days a week
Kiplinger A Step Ahead
Get practical help to make better financial decisions in your everyday life, from spending to savings on top deals.

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Closing Bell
Get today's biggest financial and investing headlines delivered to your inbox every day the U.S. stock market is open.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Adviser Intel
Financial pros across the country share best practices and fresh tactics to preserve and grow your wealth.

Delivered weekly
Kiplinger Tax Tips
Trim your federal and state tax bills with practical tax-planning and tax-cutting strategies.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Retirement Tips
Your twice-a-week guide to planning and enjoying a financially secure and richly rewarding retirement

Sent bimonthly.
Kiplinger Adviser Angle
Insights for advisers, wealth managers and other financial professionals.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Investing Weekly
Your twice-a-week roundup of promising stocks, funds, companies and industries you should consider, ones you should avoid, and why.

Sent weekly for six weeks
Kiplinger Invest for Retirement
Your step-by-step six-part series on how to invest for retirement, from devising a successful strategy to exactly which investments to choose.
If you want to track your progress toward a goal, chances are there is an app that can do that for you. For example, you can track your steps, your packages, your diet and even your family’s whereabouts.
But when it comes to saving for your retirement, how much time do you spend tracking your progress? And at what point in your life should you start paying attention?
Retirement planning can be intimidating at any age — even more so early in your career. When retirement seems so far in the future, it’s hard to plan for it with so many competing priorities in the present. For example, in addition to your regular bills, you may have student loans to repay. Or you may be trying to save money to purchase a home or save for your kids’ college education.
From just $107.88 $24.99 for Kiplinger Personal Finance
Become a smarter, better informed investor. Subscribe from just $107.88 $24.99, plus get up to 4 Special Issues

Sign up for Kiplinger’s Free Newsletters
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and more - straight to your e-mail.
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice - straight to your e-mail.
Still, it’s important to make steady progress toward saving, no matter what your age. Moreover, taking stock of where you stand can help you plan with more intention based on your situation.
So, I’m 35. What Should I Have Saved?
There is a lot of research showing that people tend to rely on approximations or rules of thumb when it comes to financial decisions.
With this in mind, many financial firms publish savings benchmarks that show the ideal levels of savings at different ages relative to an individual’s income. A savings benchmark isn’t a replacement for comprehensive planning, but it is a quick way to gauge whether you’re on track. It’s much better than the alternative some people use — blindly guessing! More importantly, it can act as a catalyst to take action and start saving more.
However, for the benchmark to be useful, it needs to be realistic. Setting the target too low can lead to a false sense of confidence; setting it too high can discourage people from doing anything. Articles on retirement savings goals have generated spirited discussion about the reasonableness of the targets.
Last year, my colleagues and I re-evaluated how to calculate achievable benchmarks. We started with the goal in mind: determining the amount of assets needed by age 65. While that number depends on a lot of factors, income is the biggest one. Since higher earners will get a smaller portion of their income in retirement from Social Security, they generally need more assets in relation to their income. We estimated that most people looking to retire around age 65 should aim for assets totaling between eight and 14 times their preretirement gross income.
From there, we identified savings benchmarks at other ages based on a reasonable trajectory of earnings and savings rates. We didn’t presume that everyone starts saving our recommended 15% of their income immediately upon receiving their first paycheck. Rather, our hypothetical investor starts saving 6% at age 25 and ramps savings up by 1 percentage point each year until reaching an appropriate level. We found that 15% of income per year (including any employer contributions) is an appropriate savings level for many people, but we recommend that higher earners aim beyond 15%.
A Look at the Benchmarks
Considering all this, here are some savings benchmarks for people in the following age groups:
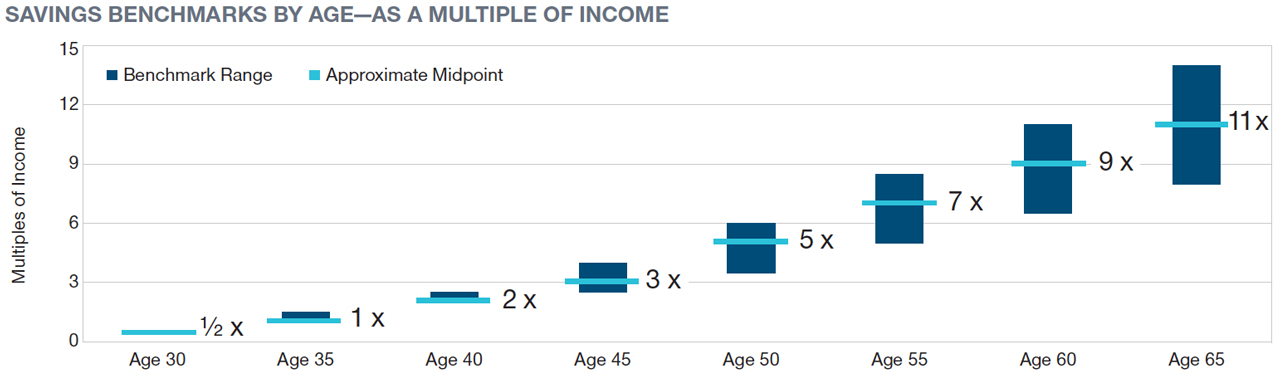
| Investor's Age | Savings Benchmarks |
|---|---|
| 30 | Half of salary saved today |
| 35 | 1x to 1.5x salary saved today |
| 40 | 2x to 2.5x salary saved today |
| 45 | 2.5x to 4x salary saved today |
| 50 | 3.5x to 6x salary saved today |
| 55 | 5x to 8.5x salary saved today |
| 60 | 6.5x to 11x salary saved today |
| 65 | 8x to 14x salary saved today |
Key Assumptions: Household income grows at 5% until age 45 and 3% (the assumed inflation rate) thereafter. Investment returns before retirement are 7% before taxes, and savings grow tax-deferred. The person retires at age 65 and begins withdrawing 4% of assets (a rate intended to support steady inflation-adjusted spending over a 30-year retirement). Savings benchmark ranges are based on individuals or couples with current household income between $75,000 and $250,000. Target multiples at retirement reflect estimated spending needs in retirement (including a 5% reduction from preretirement levels), taxes and Social Security benefits based on the ssa.gov Quick Calculator. See additional details in Are My Retirement Savings On Track?
So, to answer the question, we believe having one to one and a half times your income saved for retirement by age 35 is a reasonable target. It’s an attainable goal for someone who starts saving at age 25. For example, a 35-year-old earning $60,000 would be on track if she’s saved about $60,000 to $90,000.
The Benchmarks for Those Closer to Retirement
The range gets wider as you get older, so we also provide more detailed estimates for people approaching retirement. This helps someone find a realistic target based on age and marital status, which affects Social Security benefits.

How to Stay on Track
The point of benchmarks isn’t to make you feel superior or inadequate. It’s to prompt action, coupled with a guidepost to inform those actions, even if that means staying the course. If you’re not on track, don’t despair. Focus less on the shortfall and more on the incremental steps you can take to rectify the situation:
- Make sure you are taking advantage of the full company match in your workplace retirement plan.
- If you can increase your savings rate right away, that’s ideal. If not, gradually save more over time.
- If you have a company retirement plan that enables automatic increases, sign up.
- If you are struggling to save, many employers offer financial wellness programs or other tools that can help with budgeting and basic finances.
Use these savings benchmarks to get more comfortable with planning for retirement. Then go beyond the rule of thumb to fully understand your potential retirement expenses and income sources. Beyond your savings, think about what you are saving for and how you envision spending your time after years of hard work. After all, that’s the reason why you are saving in the first place.
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.

Roger Young is Vice President and senior financial planner with T. Rowe Price Associates in Owings Mills, Md. Roger draws upon his previous experience as a financial adviser to share practical insights on retirement and personal finance topics of interest to individuals and advisers. He has master's degrees from Carnegie Mellon University and the University of Maryland, as well as a BBA in accounting from Loyola College (Md.).
-
 Dow Leads in Mixed Session on Amgen Earnings: Stock Market Today
Dow Leads in Mixed Session on Amgen Earnings: Stock Market TodayThe rest of Wall Street struggled as Advanced Micro Devices earnings caused a chip-stock sell-off.
-
 How to Watch the 2026 Winter Olympics Without Overpaying
How to Watch the 2026 Winter Olympics Without OverpayingHere’s how to stream the 2026 Winter Olympics live, including low-cost viewing options, Peacock access and ways to catch your favorite athletes and events from anywhere.
-
 Here’s How to Stream the Super Bowl for Less
Here’s How to Stream the Super Bowl for LessWe'll show you the least expensive ways to stream football's biggest event.
-
 How to Add a Pet Trust to Your Estate Plan: Don't Leave Your Best Friend to Chance
How to Add a Pet Trust to Your Estate Plan: Don't Leave Your Best Friend to ChanceAdding a pet trust to your estate plan can ensure your pets are properly looked after when you're no longer able to care for them. This is how to go about it.
-
 Want to Avoid Leaving Chaos in Your Wake? Don't Leave Behind an Outdated Estate Plan
Want to Avoid Leaving Chaos in Your Wake? Don't Leave Behind an Outdated Estate PlanAn outdated or incomplete estate plan could cause confusion for those handling your affairs at a difficult time. This guide highlights what to update and when.
-
 I'm a Financial Adviser: This Is Why I Became an Advocate for Fee-Only Financial Advice
I'm a Financial Adviser: This Is Why I Became an Advocate for Fee-Only Financial AdviceCan financial advisers who earn commissions on product sales give clients the best advice? For one professional, changing track was the clear choice.
-
 I Met With 100-Plus Advisers to Develop This Road Map for Adopting AI
I Met With 100-Plus Advisers to Develop This Road Map for Adopting AIFor financial advisers eager to embrace AI but unsure where to start, this road map will help you integrate the right tools and safeguards into your work.
-
 The Referral Revolution: How to Grow Your Business With Trust
The Referral Revolution: How to Grow Your Business With TrustYou can attract ideal clients by focusing on value and leveraging your current relationships to create a referral-based practice.
-
 This Is How You Can Land a Job You'll Love
This Is How You Can Land a Job You'll Love"Work How You Are Wired" leads job seekers on a journey of self-discovery that could help them snag the job of their dreams.
-
 65 or Older? Cut Your Tax Bill Before the Clock Runs Out
65 or Older? Cut Your Tax Bill Before the Clock Runs OutThanks to the OBBBA, you may be able to trim your tax bill by as much as $14,000. But you'll need to act soon, as not all of the provisions are permanent.
-
 The Key to a Successful Transition When Selling Your Business: Start the Process Sooner Than You Think You Need To
The Key to a Successful Transition When Selling Your Business: Start the Process Sooner Than You Think You Need ToWay before selling your business, you can align tax strategy, estate planning, family priorities and investment decisions to create flexibility.