One Way Near-Retirees Can Ride Out a Recession
There's no reason to freak out about a recession, but stakes are different for those in the "fragile" decade. If you're worried, here's how to insure your retirement income against a bear market.


Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Today
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more delivered daily. Smart money moves start here.

Sent five days a week
Kiplinger A Step Ahead
Get practical help to make better financial decisions in your everyday life, from spending to savings on top deals.

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Closing Bell
Get today's biggest financial and investing headlines delivered to your inbox every day the U.S. stock market is open.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Adviser Intel
Financial pros across the country share best practices and fresh tactics to preserve and grow your wealth.

Delivered weekly
Kiplinger Tax Tips
Trim your federal and state tax bills with practical tax-planning and tax-cutting strategies.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Retirement Tips
Your twice-a-week guide to planning and enjoying a financially secure and richly rewarding retirement

Sent bimonthly.
Kiplinger Adviser Angle
Insights for advisers, wealth managers and other financial professionals.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Investing Weekly
Your twice-a-week roundup of promising stocks, funds, companies and industries you should consider, ones you should avoid, and why.

Sent weekly for six weeks
Kiplinger Invest for Retirement
Your step-by-step six-part series on how to invest for retirement, from devising a successful strategy to exactly which investments to choose.
Though the energy and anxiety we spend on them might suggest something more epic and frightening, recessions are simply a normal part of the economic cycle. Some are worse than others.
Certainly, those of us who lived through the Great Recession may be predisposed to some outsized worry. But recessions are healthy and necessary.
Recessions Have Some Good Points
Like the seasons, economic cycles include periods of growth and periods of depletion and rest. We shed unhealthy waste in the fall and winter of our economic cycles to make room for the green shoots and progress of cycles that follow.
From just $107.88 $24.99 for Kiplinger Personal Finance
Become a smarter, better informed investor. Subscribe from just $107.88 $24.99, plus get up to 4 Special Issues

Sign up for Kiplinger’s Free Newsletters
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and more - straight to your e-mail.
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice - straight to your e-mail.
Failing companies that struggle to make it through periods of growth finally shutter, and their employees are released back into the pool of worker talent to feed healthy future growth. Equities prices are "pruned" back, and other so-called "creative destruction" allows for new growth and innovation.
Right now, stocks are approaching historically expensive valuations, for example. A recession will make future investments cheaper, which is good in the long run. In the short term, though, the story can be a bit different. Unemployment, declining asset values and general uncertainty present different challenges for workers based on their age and how close they are to retiring.
On the investments side, for example, younger savers are more likely to be able to make up portfolio losses over their long(er) investment horizons. For a 60-something worker, the stakes are much higher.
The Fragile Decade
Weathering a recession while drawing down an asset can have a lasting negative impact on retirement income. That's why we refer to the last five working years and first five years of retirement as the "fragile decade." Unlike younger workers, folks living through their fragile decade don’t have the time to make up for losses during a downturn and may want to consider defensive positions to protect themselves from big losses.
Low-cost, next-generation annuities developed over the last few years are designed to protect investors and help usher them through the fragile decade without the onerous lock-up periods, and rigid limitations of traditional variable annuities.
Sequence of Returns Risk – the First Hurdle in Retirement
A recession early in retirement can drag your assets down as you begin simultaneously taking income. This double dip puts you at risk of outliving your assets. The impact of that same recession wouldn't be nearly as catastrophic if it happened in year 11 rather than year one of retirement.
In fact, our research has shown that if an investor's sequence of returns were inverted — from retiring during a recession, to retiring during an up market — outcomes would be markedly different. In the chart below, we look at two 15-year periods of identical returns. In the first, Investor Green retires during a five-year recession followed by a 10-year bull market. In the second, we reversed the order. Investor Blue retires during a 10-year period of growth followed by a five-year recession. These are identical annual performance numbers — though sequenced in reverse — with very different results.
That's because Investor Blue enjoys 10 years of positive returns while beginning to take income rather than the inverse. Those positive returns would offset the withdrawals, and potentially grow the asset before the negative returns begin to affect the investment.
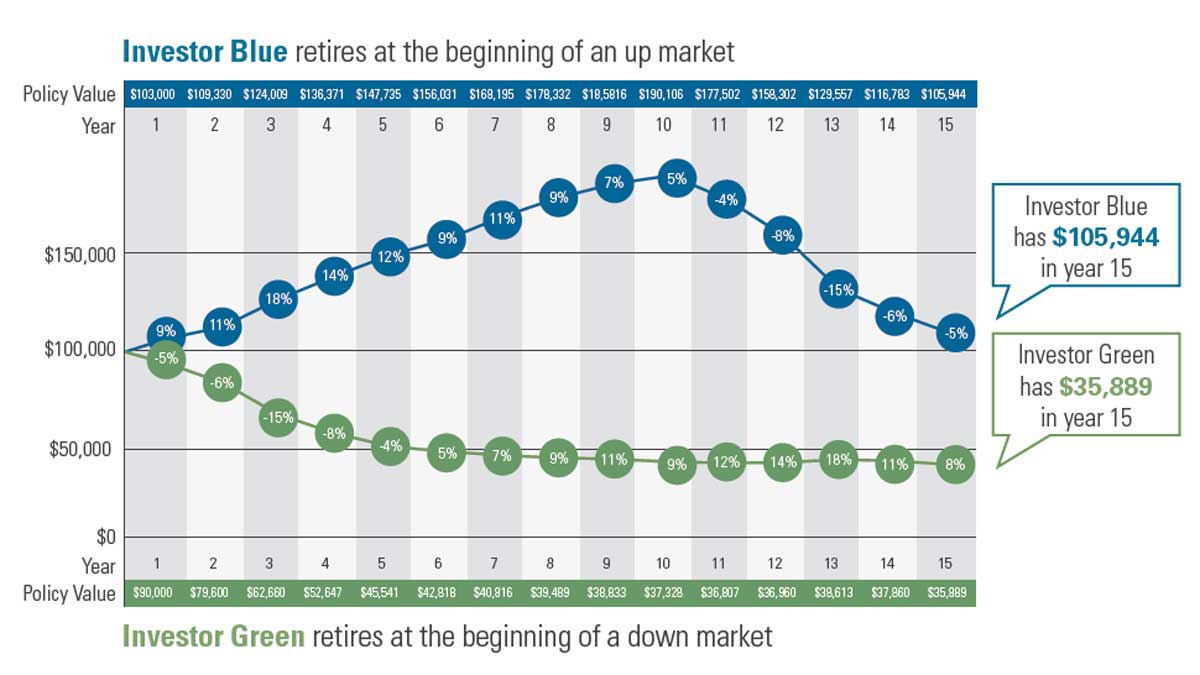
Source: RetireOne, "Sequence of Returns Risk." Please note that the simple hypothetical illustration above does not represent the results of an actual investment. It does not reflect any investment fees, expenses or taxes associated with investments. An average annual return of 4% is reflected for both investors. Annual withdrawals of $5,000 are taken at the end of each year.
The risk in the timing of poor portfolio performance and retirement income withdrawals is called "sequence of returns risk." That risk is what makes your last five working years and first five years in retirement so fragile. As such, sequence of returns risk is the first major hurdle to clear in retirement.
How to 'Insure' Your Future Income
Planning how to convert an asset into an income stream in retirement should begin at least 10 years before you begin to draw down your assets, and it could include looking into ways to "insure" your income stream against downturns. This may be especially important now, since we're in year 11 of an unprecedented bull market run that some believe may be coming to an end.
You may "insure" your future retirement income during this fragile decade by taking a portion of your assets and purchasing a variable annuity with a guaranteed lifetime withdrawal benefit ("GLWB"). The key is to invest in a low-cost, commission-free variable annuity with no surrender charges.
In this case, a variable annuity with GLWB is preferable to a single premium immediate annuity because it provides strong, guaranteed income with market participation and the ability to cancel and walk away at any time. The ability to cancel is really important because you don't want to be stuck paying for protections you no longer need.
If you buy a low-cost variable annuity with a GLWB, you may expect to pay something like 1.5% to 2% in annual fees (insurance expenses, underlying investment expenses and rider charges). This is insurance. It costs money. Once you make it to the other side of the fragile decade you may then decide to keep the GLWB rider or get rid of it and reduce your expenses. More on that in a bit.
During the deferral period — in this case the first five years, before you begin taking income — some variable annuity GLWB riders offer an annual "roll-up" that guarantees the benefit base will increase annually by a prescribed percentage regardless of what happens in the market, and ultimately to your investment.
This is the insurance component, but bear in mind that the benefit base is NOT your account value. Your account may actually lose money, and your benefit base may steadily increase. The beauty of this tactic is that the benefit base is the dollar amount upon which the insurance company bases your income payments.
Let's say that guaranteed roll up amount is 7.2% annually. After five years your benefit base would grow regardless of what happens in the market. In this example, investing $500,000 in the annuity could generate income payments based on a $708,000 benefit base (as long as you don't withdraw any money in that time).
Canceling the GLWB and/or the Variable Annuity
If your annuity performs better than 7.2% annually, then your account value equals or exceeds your benefit base, and you'll be faced with a decision about whether you even need the GLWB anymore.
Insuring the fragile decade with a variable annuity GLWB has other benefits. If you purchase the annuity contract in an IRA, you may cancel the whole annuity contract without any tax consequences and eliminate all of the expenses of the variable annuity.
It's like buying an insurance policy for your IRA assets, then canceling when you no longer need the insurance. There are no additional tax benefits associated with investing IRA assets in a variable annuity, however.
Keep in mind that if you decide to remove the GLWB rider, you'll probably have a 30-day window on one of the contract anniversaries to cancel (maybe every fifth year), and you will lose your benefit base. Your financial adviser can give you the proper guidance.
Waiting Five More Years (A Decade of Deferral)
If you can afford to wait another five years before taking income, you may have the opportunity to further improve your footing for retirement. Remember the Rule of 72? It’s a quick way of determining how long it will take for an investment to double. Divide 72 by 7.2. It would take 10 years for an investment earning a 7.2% annual rate of return to double. After 10 years your benefit base could grow to twice its original value, again, regardless of what happens in the market. In this case $500,000 could grow to a benefit base of $1 million — again, provided you don't take any withdrawals in that period.
Using a variable annuity with a GLWB can help you bridge this fragile decade, which would allow you to increase your "risk budget" and take on some additional risk in other parts of your portfolio, if necessary. If markets do well, you'll do well. If not, you will have insured yourself against an income shortfall (and longevity risk) by growing your benefit base in the GLWB rider.
When your fragile decade is in the rearview mirror, there'll be other risks to address, but, at the very least, you will have hurdled the first major obstacle to overcoming longevity risk, and that's sequence of returns risk.
Regardless of what experts think about how soon a recession may come or how bad it may be, it is no reason to panic. Some folks are simply more vulnerable than others, and should speak with their financial adviser about planning accordingly. Waiting too long to have that conversation can have lasting consequences.
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.

David Stone is founder and CEO of RetireOne™, the leading, independent platform for fee-based insurance solutions. Prior to RetireOne, David was chief legal counsel for all of Charles Schwab's insurance and risk management initiatives. He is a frequent speaker at industry conferences as well as an active participant on numerous committees dedicated to retirement income product solutions.
-
 Dow Leads in Mixed Session on Amgen Earnings: Stock Market Today
Dow Leads in Mixed Session on Amgen Earnings: Stock Market TodayThe rest of Wall Street struggled as Advanced Micro Devices earnings caused a chip-stock sell-off.
-
 How to Watch the 2026 Winter Olympics Without Overpaying
How to Watch the 2026 Winter Olympics Without OverpayingHere’s how to stream the 2026 Winter Olympics live, including low-cost viewing options, Peacock access and ways to catch your favorite athletes and events from anywhere.
-
 Here’s How to Stream the Super Bowl for Less
Here’s How to Stream the Super Bowl for LessWe'll show you the least expensive ways to stream football's biggest event.
-
 How to Add a Pet Trust to Your Estate Plan: Don't Leave Your Best Friend to Chance
How to Add a Pet Trust to Your Estate Plan: Don't Leave Your Best Friend to ChanceAdding a pet trust to your estate plan can ensure your pets are properly looked after when you're no longer able to care for them. This is how to go about it.
-
 Want to Avoid Leaving Chaos in Your Wake? Don't Leave Behind an Outdated Estate Plan
Want to Avoid Leaving Chaos in Your Wake? Don't Leave Behind an Outdated Estate PlanAn outdated or incomplete estate plan could cause confusion for those handling your affairs at a difficult time. This guide highlights what to update and when.
-
 I'm a Financial Adviser: This Is Why I Became an Advocate for Fee-Only Financial Advice
I'm a Financial Adviser: This Is Why I Became an Advocate for Fee-Only Financial AdviceCan financial advisers who earn commissions on product sales give clients the best advice? For one professional, changing track was the clear choice.
-
 I Met With 100-Plus Advisers to Develop This Road Map for Adopting AI
I Met With 100-Plus Advisers to Develop This Road Map for Adopting AIFor financial advisers eager to embrace AI but unsure where to start, this road map will help you integrate the right tools and safeguards into your work.
-
 The Referral Revolution: How to Grow Your Business With Trust
The Referral Revolution: How to Grow Your Business With TrustYou can attract ideal clients by focusing on value and leveraging your current relationships to create a referral-based practice.
-
 This Is How You Can Land a Job You'll Love
This Is How You Can Land a Job You'll Love"Work How You Are Wired" leads job seekers on a journey of self-discovery that could help them snag the job of their dreams.
-
 65 or Older? Cut Your Tax Bill Before the Clock Runs Out
65 or Older? Cut Your Tax Bill Before the Clock Runs OutThanks to the OBBBA, you may be able to trim your tax bill by as much as $14,000. But you'll need to act soon, as not all of the provisions are permanent.
-
 The Key to a Successful Transition When Selling Your Business: Start the Process Sooner Than You Think You Need To
The Key to a Successful Transition When Selling Your Business: Start the Process Sooner Than You Think You Need ToWay before selling your business, you can align tax strategy, estate planning, family priorities and investment decisions to create flexibility.