Social Security Earnings Test Ensnares a Spouse
The test can decrease family members’ Social Security benefits based on your record.

Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Today
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more delivered daily. Smart money moves start here.

Sent five days a week
Kiplinger A Step Ahead
Get practical help to make better financial decisions in your everyday life, from spending to savings on top deals.

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Closing Bell
Get today's biggest financial and investing headlines delivered to your inbox every day the U.S. stock market is open.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Adviser Intel
Financial pros across the country share best practices and fresh tactics to preserve and grow your wealth.

Delivered weekly
Kiplinger Tax Tips
Trim your federal and state tax bills with practical tax-planning and tax-cutting strategies.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Retirement Tips
Your twice-a-week guide to planning and enjoying a financially secure and richly rewarding retirement

Sent bimonthly.
Kiplinger Adviser Angle
Insights for advisers, wealth managers and other financial professionals.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Investing Weekly
Your twice-a-week roundup of promising stocks, funds, companies and industries you should consider, ones you should avoid, and why.

Sent weekly for six weeks
Kiplinger Invest for Retirement
Your step-by-step six-part series on how to invest for retirement, from devising a successful strategy to exactly which investments to choose.
You've likely heard of the dreaded “earnings test” for Social Security benefits. What’s sure to be a surprise, however, is that the earnings test squeezes not only your benefit but also family members’ benefits based on your record. And that could put a wrinkle in a couple’s plan to maximize household income by filing for a spousal benefit while delaying a higher earner’s benefit.
The earnings test hits working beneficiaries who are younger than full retirement age—age 66 for those born between 1943 and 1954. Under the earnings test, $1 of benefits is withheld for every $2 in earnings above the annual earnings limit of $15,480 in 2014. The earnings test disappears at full retirement age.
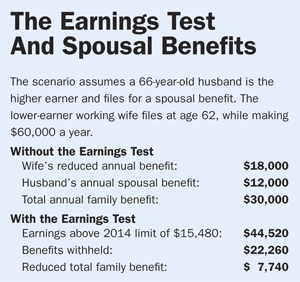
But a spouse who is full retirement age, as well as the younger wage earner, could be ensnared by the earnings test. Say the husband is the higher earner, age 66 and eligible for a full retirement benefit of $2,500 a month. He is waiting to take benefits until age 70 to earn delayed retirement credits of 8% a year—boosting his eventual benefit to $3,300 a month (see table below for the calculations).
From just $107.88 $24.99 for Kiplinger Personal Finance
Become a smarter, better informed investor. Subscribe from just $107.88 $24.99, plus get up to 4 Special Issues

Sign up for Kiplinger’s Free Newsletters
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and more - straight to your e-mail.
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice - straight to your e-mail.
In the meantime, he’d like to file a “restricted application” for a spousal benefit on his lower-earning wife’s record to boost household income. (Under this rule, a spouse who is full retirement age can choose to file for his own benefit or for a spousal benefit.) His 62-year-old wife, who is still working, would need to apply for her own benefit so that he can claim the spousal benefit. She’s eligible for a benefit of $2,000 a month at full retirement age. By claiming four years early, her benefit would be reduced to $1,500, but her husband could claim the full spousal benefit of $1,000 a month because he is full retirement age.
Here’s where the earnings test puts the kibosh on the couple’s plan. If not for the earnings test, the couple would be eligible for a total benefit amount of $30,000 for the year.
In this scenario, the wife is earning $60,000, far above the earnings limit. The earnings test claims a chunk of the husband’s benefits as well as hers. The Social Security Administration would withhold $22,260 from the total family benefit, leaving the couple with $7,740 in benefits for the year. “If any benefits are left over, no matter how small, the Social Security Administration would pay them that benefit,” says Jim Blair, a former district manager for an Ohio Social Security office and a partner at Premier Social Security Consulting, in Sharonville, Ohio.
When the wife turns full retirement age, the Social Security Administration will adjust her benefit upward to make up for her forfeited benefit. The husband’s lost spousal benefits will be gone forever.
Test Gets Easier at Full Retirement Age
Some good news: The amount a couple can receive goes up in the year the younger wife turns 66. “There’s a special rule for the earnings test for the year you hit full retirement age,” says William Reichenstein, a professor of finance at Baylor University, in Waco, Tex.
In the year you hit full retirement age, a different formula applies: One dollar in benefits will be withheld for every $3 in earnings above $41,400 in 2014. The amount a couple receives would jump significantly.
The earnings test disappears starting the month you turn full retirement age. If the younger spouse has a birthday early in the year, the couple will get the full amount of benefits that much faster. “If her birthday is early in the year, there’s only a few months the earnings test applies,” says Blair.
If she turns 66 in March, for instance, the earnings test would apply only for January and February. She “wouldn’t have earned enough to exceed the test,” says Reichenstein. And as of her birthday month, she can earn as much as she likes without affecting her benefit or her husband’s spousal benefit.
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.

-
 Dow Leads in Mixed Session on Amgen Earnings: Stock Market Today
Dow Leads in Mixed Session on Amgen Earnings: Stock Market TodayThe rest of Wall Street struggled as Advanced Micro Devices earnings caused a chip-stock sell-off.
-
 How to Watch the 2026 Winter Olympics Without Overpaying
How to Watch the 2026 Winter Olympics Without OverpayingHere’s how to stream the 2026 Winter Olympics live, including low-cost viewing options, Peacock access and ways to catch your favorite athletes and events from anywhere.
-
 Here’s How to Stream the Super Bowl for Less
Here’s How to Stream the Super Bowl for LessWe'll show you the least expensive ways to stream football's biggest event.
-
 9 Types of Insurance You Probably Don't Need
9 Types of Insurance You Probably Don't NeedFinancial Planning If you're paying for these types of insurance, you may be wasting your money. Here's what you need to know.
-
 Amazon Resale: Where Amazon Prime Returns Become Your Online Bargains
Amazon Resale: Where Amazon Prime Returns Become Your Online BargainsFeature Amazon Resale products may have some imperfections, but that often leads to wildly discounted prices.
-
 457 Plan Contribution Limits for 2026
457 Plan Contribution Limits for 2026Retirement plans There are higher 457 plan contribution limits in 2026. That's good news for state and local government employees.
-
 Medicare Basics: 12 Things You Need to Know
Medicare Basics: 12 Things You Need to KnowMedicare There's Medicare Part A, Part B, Part D, Medigap plans, Medicare Advantage plans and so on. We sort out the confusion about signing up for Medicare — and much more.
-
 The Seven Worst Assets to Leave Your Kids or Grandkids
The Seven Worst Assets to Leave Your Kids or Grandkidsinheritance Leaving these assets to your loved ones may be more trouble than it’s worth. Here's how to avoid adding to their grief after you're gone.
-
 SEP IRA Contribution Limits for 2026
SEP IRA Contribution Limits for 2026SEP IRA A good option for small business owners, SEP IRAs allow individual annual contributions of as much as $70,000 in 2025, and up to $72,000 in 2026.
-
 Roth IRA Contribution Limits for 2026
Roth IRA Contribution Limits for 2026Roth IRAs Roth IRAs allow you to save for retirement with after-tax dollars while you're working, and then withdraw those contributions and earnings tax-free when you retire. Here's a look at 2026 limits and income-based phaseouts.
-
 SIMPLE IRA Contribution Limits for 2026
SIMPLE IRA Contribution Limits for 2026simple IRA For 2026, the SIMPLE IRA contribution limit rises to $17,000, with a $4,000 catch-up for those 50 and over, totaling $21,000.