A Financial Guide to Gray Divorce for Women
Older women deal with many of the same issues as their younger counterparts but face additional challenges, some unexpected during a gray divorce.


Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Today
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more delivered daily. Smart money moves start here.

Sent five days a week
Kiplinger A Step Ahead
Get practical help to make better financial decisions in your everyday life, from spending to savings on top deals.

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Closing Bell
Get today's biggest financial and investing headlines delivered to your inbox every day the U.S. stock market is open.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Adviser Intel
Financial pros across the country share best practices and fresh tactics to preserve and grow your wealth.

Delivered weekly
Kiplinger Tax Tips
Trim your federal and state tax bills with practical tax-planning and tax-cutting strategies.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Retirement Tips
Your twice-a-week guide to planning and enjoying a financially secure and richly rewarding retirement

Sent bimonthly.
Kiplinger Adviser Angle
Insights for advisers, wealth managers and other financial professionals.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Investing Weekly
Your twice-a-week roundup of promising stocks, funds, companies and industries you should consider, ones you should avoid, and why.

Sent weekly for six weeks
Kiplinger Invest for Retirement
Your step-by-step six-part series on how to invest for retirement, from devising a successful strategy to exactly which investments to choose.
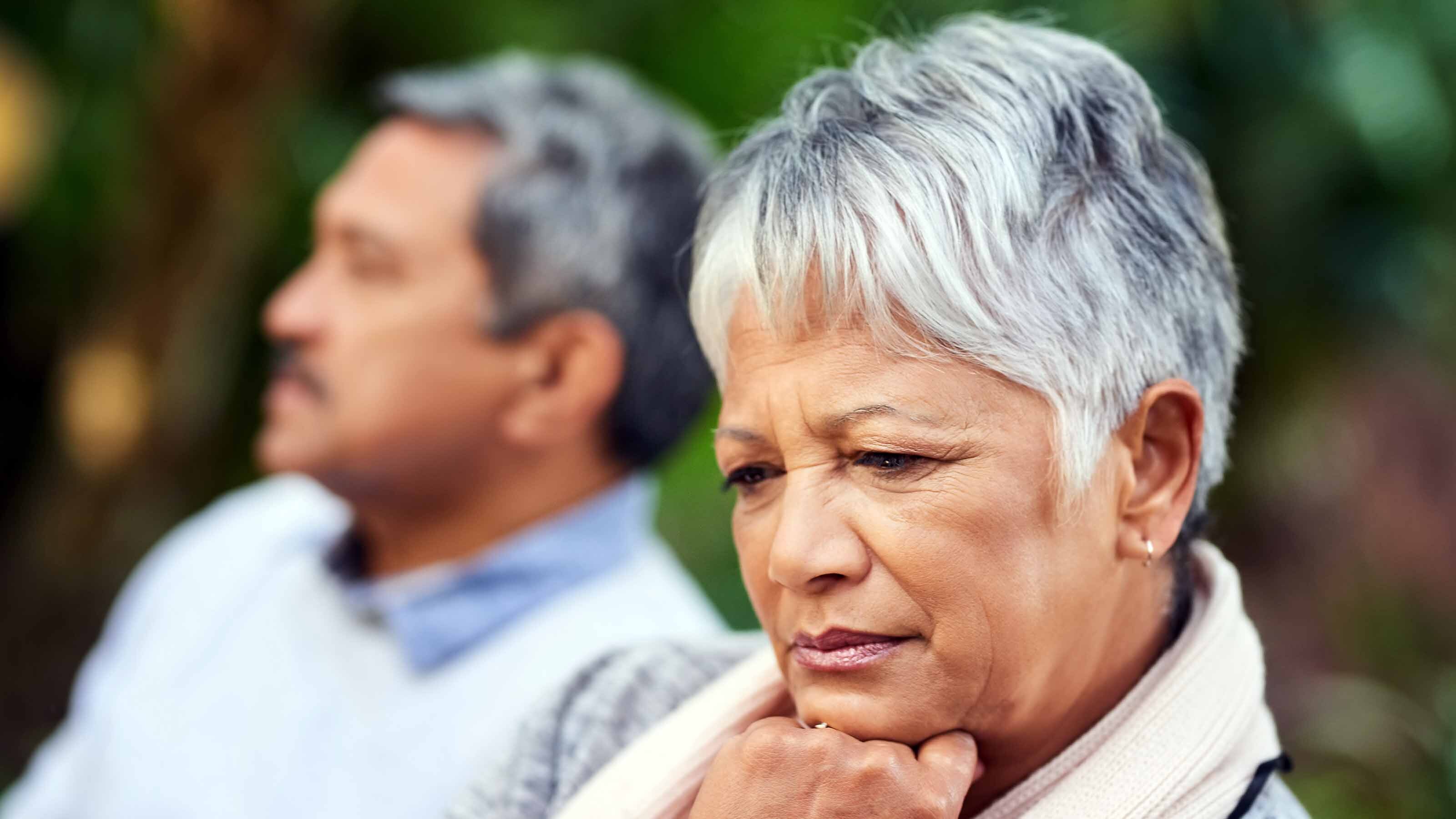
Even though a later-in-life divorce, often referred to as a "gray divorce," can be potentially devastating financially, it’s often women who initiate the process. “They may have stayed in an unhappy marriage for the sake of the children,” says Lisa Zeiderman, managing partner at the law firm Miller Zeiderman, in New York City. “Now that the children are off to college or grown, they feel it’s time to move on with their lives.”
Sometimes the breaking-up point comes when both spouses retire and “sparks start to fly,” says Kimberly Foss, a partner with Mercer Global Advisors in Roseville, Calif, of the reasons for a gray divorce. Leslie Thompson, cofounder of Spectrum Wealth Management in Indianapolis, says financial control is often a factor for women “who don’t want to be judged on how they manage their money.”
The topic of gray divorce hit daytime television this week as Kelly Ripa discussed it — sitting next to her husband and co-host, Mark Consuelos — on "Live With Kelly and Mark." This was not a divorce announcement, as the pair demonstrated they're still happily partners, but an acknowledgement of the recent rise in later-in-life divorce rates and curiosity in why that's happening.
From just $107.88 $24.99 for Kiplinger Personal Finance
Become a smarter, better informed investor. Subscribe from just $107.88 $24.99, plus get up to 4 Special Issues

Sign up for Kiplinger’s Free Newsletters
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and more - straight to your e-mail.
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice - straight to your e-mail.
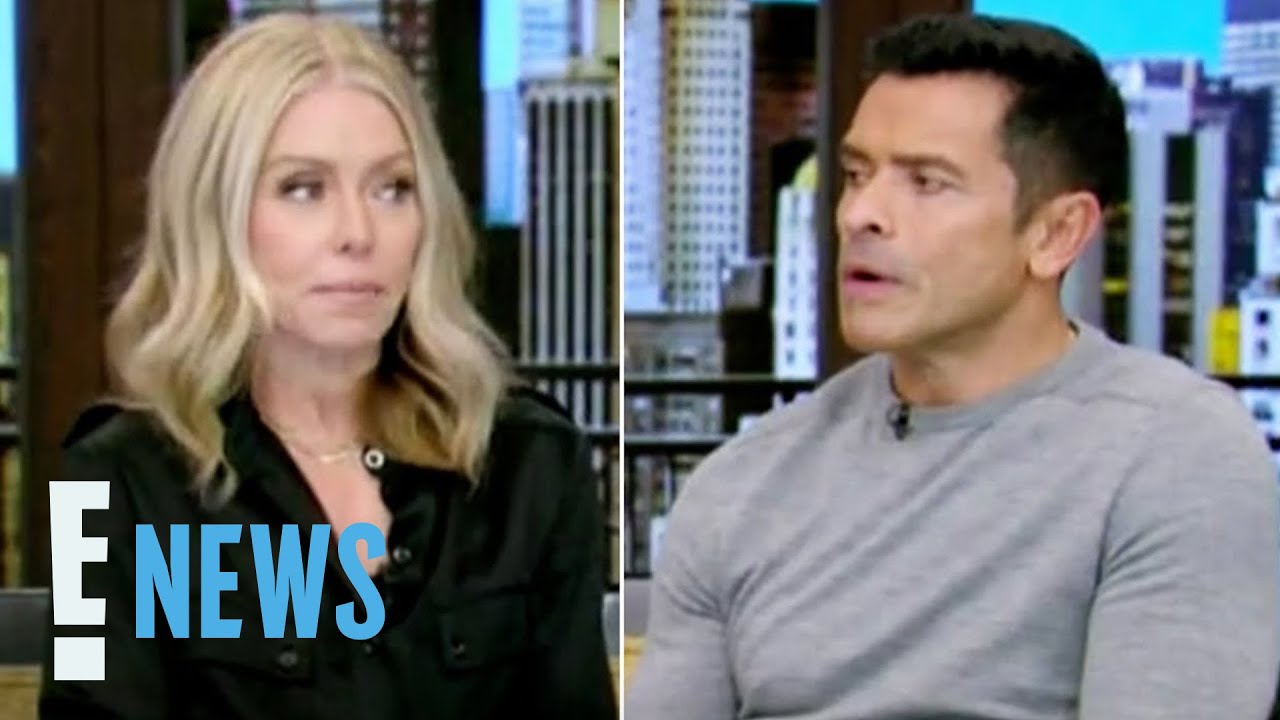
While Ripa's situation may be quite different from the average 54-year-old as a successful talk show host, in a divorce, money can be an even bigger stumbling block for older women than for younger ones.
Women in this age group frequently have been out of the paid workforce for long periods of time and “don’t have the earning capacity to find a job with an income that’s comparable to their ex-spouse’s,” says Zeiderman. Nor do they always have the time to reinvent themselves. At the same time, the available assets in the marriage have to support two households rather than one, and expenses have jumped with inflation.
Financially, says Thompson, it can be a scarier time for women in their fifties, who need to plan for the next half of their lives, than for women in their seventies, who have a shorter time frame and may have access to other resources.
Money matters in a gray divorce
Whatever your age, it’s critical to get your ducks in a row if you are considering filing for divorce and to be as prepared as possible if you are blindsided. Have credit in your own name. Hold assets in your own name. Keep a foot in the workplace door. If you aren’t working outside the home, fund a spousal IRA based on your spouse’s earnings.
And know where the money is. Zeiderman and her husband have been married for 25 years and, she says, “I trust him implicitly.” But they have what they call the “mailbox rule.” When they are at home on Saturday mornings, she opens all the mail, looks at all the statements and starts a discussion about where they stand financially.
Don’t count on receiving spousal support. Laws vary from state to state, and court-ordered alimony “is much less of a given than it used to be,” says Foss. “More often I’m seeing it as part of a settlement agreement.”
So it’s important to uncover as many assets as possible that can be used for your support and to make sure those assets are divided equitably. It may make sense to sell the family home while you still qualify for the $500,000 capital gains exclusion as a couple and invest the proceeds in income-producing assets. When divvying up joint brokerage accounts on which capital gains taxes may be due, make sure that the tax bill is also divided equitably.
If you have been married for 10 years or more, when you turn 62 you are eligible for Social Security benefits based on your ex-spouse’s earnings if they are higher than benefits based on your own earnings. But remember: A portion of the benefits may be taxable. “That’s an eye-opener for many women,” says Foss. See more in our article on how a gray divorce affects Social Security benefits.
With money such a big issue, you’ll need a budget that reflects your income and expenses so you know what kind of lifestyle you can afford.
One thing that likely won’t be a factor for older women is children. “Once children are 21, the courts won’t look at them unless they have special needs,” says Zeiderman. “Once you’re divorced, the oxygen-mask rule takes over,” she says. “Think of yourself first.”
Related content
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.

Janet Bodnar is editor-at-large of Kiplinger's Personal Finance, a position she assumed after retiring as editor of the magazine after eight years at the helm. She is a nationally recognized expert on the subjects of women and money, children's and family finances, and financial literacy. She is the author of two books, Money Smart Women and Raising Money Smart Kids. As editor-at-large, she writes two popular columns for Kiplinger, "Money Smart Women" and "Living in Retirement." Bodnar is a graduate of St. Bonaventure University and is a member of its Board of Trustees. She received her master's degree from Columbia University, where she was also a Knight-Bagehot Fellow in Business and Economics Journalism.
-
 5 Vince Lombardi Quotes Retirees Should Live By
5 Vince Lombardi Quotes Retirees Should Live ByThe iconic football coach's philosophy can help retirees win at the game of life.
-
 The $200,000 Olympic 'Pension' is a Retirement Game-Changer for Team USA
The $200,000 Olympic 'Pension' is a Retirement Game-Changer for Team USAThe donation by financier Ross Stevens is meant to be a "retirement program" for Team USA Olympic and Paralympic athletes.
-
 10 Cheapest Places to Live in Colorado
10 Cheapest Places to Live in ColoradoProperty Tax Looking for a cozy cabin near the slopes? These Colorado counties combine reasonable house prices with the state's lowest property tax bills.
-
 5 Vince Lombardi Quotes Retirees Should Live By
5 Vince Lombardi Quotes Retirees Should Live ByThe iconic football coach's philosophy can help retirees win at the game of life.
-
 The $200,000 Olympic 'Pension' is a Retirement Game-Changer for Team USA
The $200,000 Olympic 'Pension' is a Retirement Game-Changer for Team USAThe donation by financier Ross Stevens is meant to be a "retirement program" for Team USA Olympic and Paralympic athletes.
-
 How to Turn Your 401(k) Into A Real Estate Empire — Without Killing Your Retirement
How to Turn Your 401(k) Into A Real Estate Empire — Without Killing Your RetirementTapping your 401(k) to purchase investment properties is risky, but it could deliver valuable rental income in your golden years.
-
 My First $1 Million: Retired Nuclear Power Plant Supervisor, 68, Wisconsin
My First $1 Million: Retired Nuclear Power Plant Supervisor, 68, WisconsinEver wonder how someone who's made a million dollars or more did it? Kiplinger's My First $1 Million series uncovers the answers.
-
 Don't Bury Your Kids in Taxes: How to Position Your Investments to Help Create More Wealth for Them
Don't Bury Your Kids in Taxes: How to Position Your Investments to Help Create More Wealth for ThemTo minimize your heirs' tax burden, focus on aligning your investment account types and assets with your estate plan, and pay attention to the impact of RMDs.
-
 Are You 'Too Old' to Benefit From an Annuity?
Are You 'Too Old' to Benefit From an Annuity?Probably not, even if you're in your 70s or 80s, but it depends on your circumstances and the kind of annuity you're considering.
-
 In Your 50s and Seeing Retirement in the Distance? What You Do Now Can Make a Significant Impact
In Your 50s and Seeing Retirement in the Distance? What You Do Now Can Make a Significant ImpactThis is the perfect time to assess whether your retirement planning is on track and determine what steps you need to take if it's not.
-
 Your Retirement Isn't Set in Stone, But It Can Be a Work of Art
Your Retirement Isn't Set in Stone, But It Can Be a Work of ArtSetting and forgetting your retirement plan will make it hard to cope with life's challenges. Instead, consider redrawing and refining your plan as you go.