Collar Investing Strategy Can Help Protect Your Nest Egg
Here are some key considerations for using the collar strategy of put options and covered calls to safeguard your wealth in retirement.


Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Today
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more delivered daily. Smart money moves start here.

Sent five days a week
Kiplinger A Step Ahead
Get practical help to make better financial decisions in your everyday life, from spending to savings on top deals.

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Closing Bell
Get today's biggest financial and investing headlines delivered to your inbox every day the U.S. stock market is open.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Adviser Intel
Financial pros across the country share best practices and fresh tactics to preserve and grow your wealth.

Delivered weekly
Kiplinger Tax Tips
Trim your federal and state tax bills with practical tax-planning and tax-cutting strategies.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Retirement Tips
Your twice-a-week guide to planning and enjoying a financially secure and richly rewarding retirement

Sent bimonthly.
Kiplinger Adviser Angle
Insights for advisers, wealth managers and other financial professionals.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Investing Weekly
Your twice-a-week roundup of promising stocks, funds, companies and industries you should consider, ones you should avoid, and why.

Sent weekly for six weeks
Kiplinger Invest for Retirement
Your step-by-step six-part series on how to invest for retirement, from devising a successful strategy to exactly which investments to choose.
Retirement is a phase where you focus on preserving wealth rather than growing it. After years of saving, it's time to protect your hard-earned nest egg from market downturns.
Traditional protection strategies like diversification can mitigate risk. However, the collar strategy offers a direct yet flexible and dynamic way to protect your savings from potential losses while allowing income generation.
In this article, we'll dive into how the collar works and why it might be a valuable tool for retirees. We'll list the key considerations you should consider when implementing this approach. Whether you're in retirement or nearing retirement, learning about this strategy can help you safeguard your wealth.
From just $107.88 $24.99 for Kiplinger Personal Finance
Become a smarter, better informed investor. Subscribe from just $107.88 $24.99, plus get up to 4 Special Issues

Sign up for Kiplinger’s Free Newsletters
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and more - straight to your e-mail.
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice - straight to your e-mail.
The collar strategy is a popular options trading technique that involves two components: buying a put option and selling a covered call. While this may seem complex, a collar's purpose is relatively straightforward: It defines a price range within which a stock may fluctuate while offering protection against significant losses.
Let's look at the collar
The put option (protection). A put option gives you the right but not the obligation to sell your shares at a predetermined price called the strike price. It's a kind of insurance. If the stock price goes down beyond the strike price, the value of the put increases, helping offset losses on the shares. The put option sets a floor under your stock position, limiting how much you can lose if the stock goes down.
The covered call (income generation). In exchange for selling a call that gives someone the right to buy your shares at a specific strike price, you receive a premium upfront. This is what makes the call "covered," as you already own the shares you're agreeing to sell at a price above the current price in the market at a specific time in the future. While this limits your upside, the premium you can earn can act as a steady income stream to offset the cost of the put option protection premium.
Together, these two options, a long put and a short call, create a "collar" around the stock price, capping potential upside and downside. In falling markets, this strategy offers protection that could be comforting for retirees who want to avoid significant portfolio losses.
Why the collar strategy is especially important for retirees
For retirees, market downturns can feel particularly hurtful, as there is less time to recover from losses. By employing the collar strategy, retirees can create predictability and control for their portfolios.
Key benefits of using a collar strategy in retirement:
Risk management. The primary goal for retirees is to avoid significant losses. The collar strategy defines a price range for your stock's performance, limiting how far the price can fall. However, it also limits how far up you can participate in profits. The put option acts as a safety net at the put's strike price, ensuring that even if the market experiences a significant downturn through the strike price, you won't face losses after that point.
Steady income offsetting cost of protection. The covered call component of the collar strategy provides income as the premium earned can be collected at the outset of the trade. This can be particularly useful when preserving income becomes a priority in retirement. If the stock price remains relatively stable, you can continue collecting premiums through a series of covered call sales.
Predictability and control. The collar strategy establishes a clear upper and lower boundary for your stock's profits and losses, which offers a sense of predictability that is often difficult to find in the stock market. This can be especially good for retirees who prefer a more conservative investment approach.
A real-world example: protecting an Nvidia (NVDA) position. Let's say you had a significant holding in NVDA, a popular stock with a history of volatility and growth. You are concerned about potential market downturns but still want to maintain a position in the stock. Implementing the collar strategy can help you balance these objectives:
- Step 1: Buy a put option. Suppose NVDA is currently trading at $250 per share. You purchase a put option with a strike price of $230. If the stock price falls below $230, you have the right to sell your shares at $230, limiting your downside.
- Step 2: Sell a covered call. At the same time, you sell a covered call with a strike price of $270. In exchange for granting the buyer the right to purchase your NVDA shares at $270, you receive a premium upfront. However, if the stock price rises above $270, you may have to sell your shares at that price, capping your upside potential.
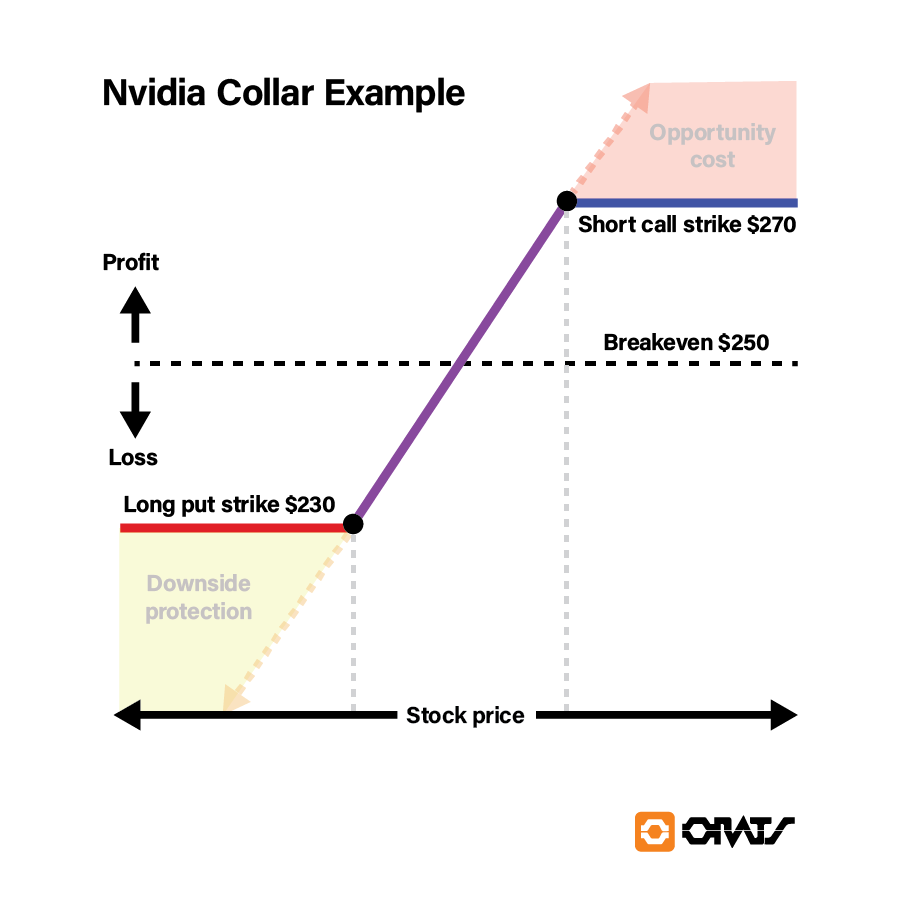
In this scenario, you have defined the minimum and maximum prices at which you will trade NVDA stock, protecting yourself from a significant loss while still earning income. This "collar" balances risk management and the desire for growth.
Critical considerations for the collar strategy
Several important factors should be considered before trying the collar strategy. While the strategy offers benefits, it's not without its complexities.
- Cost of the put option. The price of the put option varies depending on the strike price, expiration date and overall market volatility. If the put cost is too high, it could eat into the portfolio value for this protection. Alternatively, suppose the collar strategy seeks to match the premium of the call collected with the premium of the put paid out. In that case, an expensive put will cause the call to be closer to the money, and less upside participation will ensue.
- Limited upside. The collar strategy limits potential gains, which may not be ideal if the stock performs well. In our NVDA example, if the price skyrockets to $300 or higher, you'll miss out on growth beyond $270, as you are obligated to sell the stock at that price.
- Complexity of options trading. While the collar strategy is relatively straightforward compared to more advanced options strategies, it's still important to understand the mechanics of options contracts. Consulting with a financial adviser or options expert can help ensure that you're executing the strategy correctly and in a way that aligns with your overall financial goals.
Is the collar strategy right for your retirement plan?
The collar strategy can be a valuable tool for retirees looking to protect their portfolios from downside risk while remaining income- and expense-neutral. However, it's not a one-size-fits-all solution. The strategy is best suited for individuals comfortable with options trading and looking for a defined range of risk and reward.
If you need help determining whether the collar strategy aligns with your retirement goals, consulting with a financial adviser can help. They can provide personalized guidance on implementing the plan effectively and make adjustments based on your financial situation.
Retirement is a time to enjoy the fruits of your labor, not to worry about market downturns eroding your savings. The collar strategy offers a way to protect your nest egg from significant losses while still allowing for some upside participation. By defining an explicit range for your stock profits and losses, this strategy creates predictability and control, both of which are valuable assets in retirement.
As with any investment strategy, it's essential to understand the risks and complexities involved. Consulting with a professional before making any decisions can help ensure that the collar strategy is implemented in a way that aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
Related Content
- Five Building Blocks for a Sound Investment Strategy
- Want to Get Rich and Stay Rich? Avoid 10 Investing Mistakes
- Mutual Funds Reality Check: Are You Really Diversified?
- Taming Risk: Offensive vs Defensive Investing Strategies
- Tips for Honing Your Bond Investing Strategy
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.

Matt Amberson is the Principal and Founder of Option Research & Technology Services. ORATS was born out of a need by traders to get access to more accurate and realistic option research. Matt started ORATS to support his options market making firm where he would hire statistically minded individuals, put them on the floor and develop research to aid in trading options.
-
 The New Reality for Entertainment
The New Reality for EntertainmentThe Kiplinger Letter The entertainment industry is shifting as movie and TV companies face fierce competition, fight for attention and cope with artificial intelligence.
-
 Stocks Sink With Alphabet, Bitcoin: Stock Market Today
Stocks Sink With Alphabet, Bitcoin: Stock Market TodayA dismal round of jobs data did little to lift sentiment on Thursday.
-
 Betting on Super Bowl 2026? New IRS Tax Changes Could Cost You
Betting on Super Bowl 2026? New IRS Tax Changes Could Cost YouTaxable Income When Super Bowl LX hype fades, some fans may be surprised to learn that sports betting tax rules have shifted.
-
 Stocks Sink With Alphabet, Bitcoin: Stock Market Today
Stocks Sink With Alphabet, Bitcoin: Stock Market TodayA dismal round of jobs data did little to lift sentiment on Thursday.
-
 Your Adult Kids Are Doing Fine. Is It Time To Spend Some of Their Inheritance?
Your Adult Kids Are Doing Fine. Is It Time To Spend Some of Their Inheritance?If your kids are successful, do they need an inheritance? Ask yourself these four questions before passing down another dollar.
-
 The 4 Estate Planning Documents Every High-Net-Worth Family Needs (Not Just a Will)
The 4 Estate Planning Documents Every High-Net-Worth Family Needs (Not Just a Will)The key to successful estate planning for HNW families isn't just drafting these four documents, but ensuring they're current and immediately accessible.
-
 Love and Legacy: What Couples Rarely Talk About (But Should)
Love and Legacy: What Couples Rarely Talk About (But Should)Couples who talk openly about finances, including estate planning, are more likely to head into retirement joyfully. How can you get the conversation going?
-
 How to Get the Fair Value for Your Shares When You Are in the Minority Vote on a Sale of Substantially All Corporate Assets
How to Get the Fair Value for Your Shares When You Are in the Minority Vote on a Sale of Substantially All Corporate AssetsWhen a sale of substantially all corporate assets is approved by majority vote, shareholders on the losing side of the vote should understand their rights.
-
 Dow Leads in Mixed Session on Amgen Earnings: Stock Market Today
Dow Leads in Mixed Session on Amgen Earnings: Stock Market TodayThe rest of Wall Street struggled as Advanced Micro Devices earnings caused a chip-stock sell-off.
-
 We're 62 With $1.4 Million. I Want to Sell Our Beach House to Retire Now, But My Wife Wants to Keep It and Work Until 70.
We're 62 With $1.4 Million. I Want to Sell Our Beach House to Retire Now, But My Wife Wants to Keep It and Work Until 70.I want to sell the $610K vacation home and retire now, but my wife envisions a beach retirement in 8 years. We asked financial advisers to weigh in.
-
 How to Add a Pet Trust to Your Estate Plan: Don't Leave Your Best Friend to Chance
How to Add a Pet Trust to Your Estate Plan: Don't Leave Your Best Friend to ChanceAdding a pet trust to your estate plan can ensure your pets are properly looked after when you're no longer able to care for them. This is how to go about it.