Non-Qualified Annuities: Should Retirees Think Twice?
A twist many don’t see coming is that earnings from non-qualified annuities are taxed as ordinary income rather than at more favorable capital gains tax rates.


Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Today
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more delivered daily. Smart money moves start here.

Sent five days a week
Kiplinger A Step Ahead
Get practical help to make better financial decisions in your everyday life, from spending to savings on top deals.

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Closing Bell
Get today's biggest financial and investing headlines delivered to your inbox every day the U.S. stock market is open.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Adviser Intel
Financial pros across the country share best practices and fresh tactics to preserve and grow your wealth.

Delivered weekly
Kiplinger Tax Tips
Trim your federal and state tax bills with practical tax-planning and tax-cutting strategies.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Retirement Tips
Your twice-a-week guide to planning and enjoying a financially secure and richly rewarding retirement

Sent bimonthly.
Kiplinger Adviser Angle
Insights for advisers, wealth managers and other financial professionals.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Investing Weekly
Your twice-a-week roundup of promising stocks, funds, companies and industries you should consider, ones you should avoid, and why.

Sent weekly for six weeks
Kiplinger Invest for Retirement
Your step-by-step six-part series on how to invest for retirement, from devising a successful strategy to exactly which investments to choose.
Picture this: You're on the cusp of retirement, and you've just learned about a financial tool that promises to shield your hard-earned savings from taxes until you need them.
This tool is the non-qualified annuity, an insurance contract funded with after-tax money that defers taxes on your income and growth until withdrawn.
Sounds like an easy decision, right?
From just $107.88 $24.99 for Kiplinger Personal Finance
Become a smarter, better informed investor. Subscribe from just $107.88 $24.99, plus get up to 4 Special Issues

Sign up for Kiplinger’s Free Newsletters
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and more - straight to your e-mail.
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice - straight to your e-mail.
Hold that thought ...
In a world devoid of pensions, 401(k)s and similar employer-sponsored plans have become many Americans' go-to retirement saving option. These plans offer upfront tax breaks and deferred taxation on earnings, a seemingly ideal combination.
But there's a catch.
Every dollar withdrawn from a tax-deferred account is taxed as ordinary income — the least-favorable type of income tax there is.
An unfortunate surprise for many
Now, let's circle back to non-qualified annuities. By opting for one, you're essentially converting all potential long-term capital gains (which enjoy favorable tax treatment) into ordinary income, thus increasing your tax burden when those gains are withdrawn. It's an unfortunate twist many don't see coming and are unaware of when buying a non-qualified annuity.
Consider this scenario: You're a modern-day retiree with a diverse portfolio of investments — most of which have been saved in tax-deferred accounts, some in tax-preferential accounts and a small amount in tax-free accounts. Adding a non-qualified annuity might seem prudent, especially if you are a tax-sensitive investor. But if your retirement nest egg is already concentrated in tax-deferred accounts, that type of annuity will only make your future tax exposure less diverse.
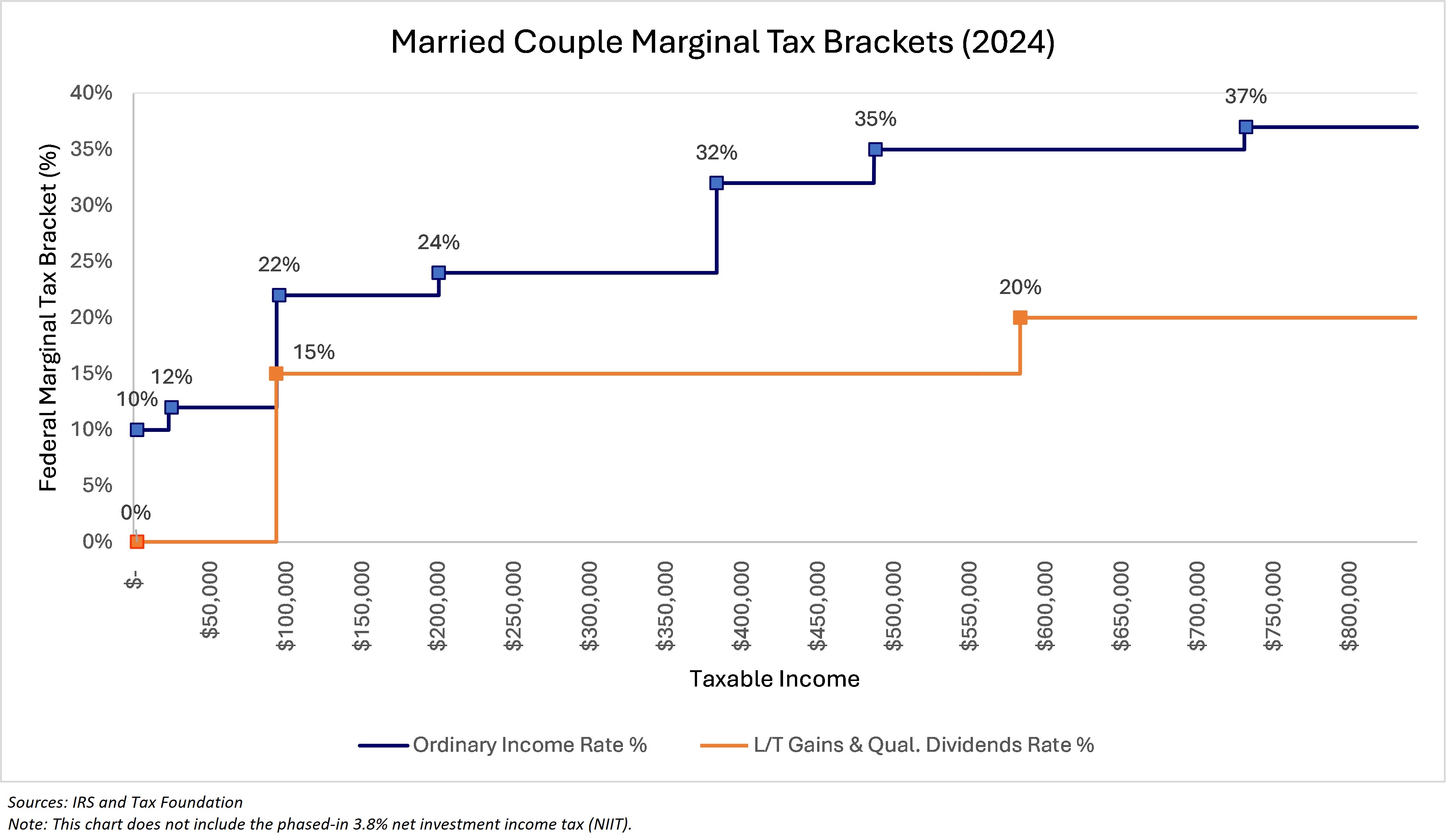
As you can see in the chart below, ordinary income tax rates (blue) are generally higher than tax rates on long-term capital gains and qualified dividends issued by stocks (orange), which is why it is advantageous for today's retirees to preserve their non-tax-deferred assets rather than convert them:
Before jumping into a non-qualified annuity, ask yourself:
How diversified is my tax exposure in retirement? Don't just diversify your investments; diversify your future tax liabilities. On the day you retire, aim to have your savings split into equal thirds among tax-deferred, tax-preferential and tax-free accounts. This lets you choose which accounts to withdraw from each year to achieve the lowest tax rate.
What does my retirement withdrawal plan look like? If you anticipate needing all your savings for retirement expenses, it’s likely advantageous to keep your taxable investment accounts due to their favorable tax treatment rather than shifting that money into another tax-deferred option like a non-qualified annuity.
Will my retirement lifestyle push me into the highest tax brackets? If yes, it would be wise to reconsider piling more money into tax-deferred savings. If not, then the tax-deferred benefits of a non-qualified annuity may fit your situation well.
Do you care about maximizing your financial legacy? Taxable brokerage accounts left to your heirs receive a step-up in basis upon your death. This is a major tax benefit for heirs that adjusts the principal in your account (cost basis) to the fair market value of your investments on the date of your death. In some cases, this can lead to thousands of dollars in capital gains taxes being forgiven. Alternatively, even though it is funded with after-tax dollars, a non-qualified annuity does not receive a “step-up in basis” upon your death. This is a major downfall of the non-qualified annuity, in my opinion.
Based on my experience …
From my experience as a financial adviser, I've found that the retirees who need to withdraw most of their savings to afford their lifestyle in retirement are better off nurturing their after-tax investments in taxable brokerage or tax-free accounts rather than piling more into the tax-deferred bucket. Next to health care costs, income taxes are a retiree's most significant expense. The goal is to minimize your income taxes as much as possible.
Although a non-qualified annuity offers immediate tax relief, it can lead to a higher tax burden in the long run. A wiser approach may be to focus on preserving your non-tax-deferred savings. This doesn't make non-qualified annuities bad financial instruments. It just means the decision to use one in your financial situation requires careful consideration from a variety of perspectives.
Advisory services offered through Wealth Enhancement Advisory Services, LLC, a registered investment advisor and affiliate of Wealth Enhancement Group®.
Related Content
- Do You Have at Least $1 Million in Tax-Deferred Investments?
- From Tax-Deferred to Tax-Free: Navigating Taxes in Retirement
- Why So Many Experts Consider Annuities a Win for Retirees
- To Create a Happy Retirement, Start With the Three Ps
- Five Common Retirement Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.

Doug is a CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER™ who guides families toward a secure retirement, ensuring their wealth is preserved and desired lifestyle is sustainable. He leads an advisory team at Wealth Enhancement Group, an independent RIA that has consistently been named as a Barron’s Top 100 RIA Firm. His team is based in Fairfield County, Conn.
-
 5 Vince Lombardi Quotes Retirees Should Live By
5 Vince Lombardi Quotes Retirees Should Live ByThe iconic football coach's philosophy can help retirees win at the game of life.
-
 The $200,000 Olympic 'Pension' is a Retirement Game-Changer for Team USA
The $200,000 Olympic 'Pension' is a Retirement Game-Changer for Team USAThe donation by financier Ross Stevens is meant to be a "retirement program" for Team USA Olympic and Paralympic athletes.
-
 10 Cheapest Places to Live in Colorado
10 Cheapest Places to Live in ColoradoProperty Tax Looking for a cozy cabin near the slopes? These Colorado counties combine reasonable house prices with the state's lowest property tax bills.
-
 Don't Bury Your Kids in Taxes: How to Position Your Investments to Help Create More Wealth for Them
Don't Bury Your Kids in Taxes: How to Position Your Investments to Help Create More Wealth for ThemTo minimize your heirs' tax burden, focus on aligning your investment account types and assets with your estate plan, and pay attention to the impact of RMDs.
-
 Are You 'Too Old' to Benefit From an Annuity?
Are You 'Too Old' to Benefit From an Annuity?Probably not, even if you're in your 70s or 80s, but it depends on your circumstances and the kind of annuity you're considering.
-
 In Your 50s and Seeing Retirement in the Distance? What You Do Now Can Make a Significant Impact
In Your 50s and Seeing Retirement in the Distance? What You Do Now Can Make a Significant ImpactThis is the perfect time to assess whether your retirement planning is on track and determine what steps you need to take if it's not.
-
 Your Retirement Isn't Set in Stone, But It Can Be a Work of Art
Your Retirement Isn't Set in Stone, But It Can Be a Work of ArtSetting and forgetting your retirement plan will make it hard to cope with life's challenges. Instead, consider redrawing and refining your plan as you go.
-
 The Bear Market Protocol: 3 Strategies to Consider in a Down Market
The Bear Market Protocol: 3 Strategies to Consider in a Down MarketThe Bear Market Protocol: 3 Strategies for a Down Market From buying the dip to strategic Roth conversions, there are several ways to use a bear market to your advantage — once you get over the fear factor.
-
 For the 2% Club, the Guardrails Approach and the 4% Rule Do Not Work: Here's What Works Instead
For the 2% Club, the Guardrails Approach and the 4% Rule Do Not Work: Here's What Works InsteadFor retirees with a pension, traditional withdrawal rules could be too restrictive. You need a tailored income plan that is much more flexible and realistic.
-
 Retiring Next Year? Now Is the Time to Start Designing What Your Retirement Will Look Like
Retiring Next Year? Now Is the Time to Start Designing What Your Retirement Will Look LikeThis is when you should be shifting your focus from growing your portfolio to designing an income and tax strategy that aligns your resources with your purpose.
-
 I'm a Financial Planner: This Layered Approach for Your Retirement Money Can Help Lower Your Stress
I'm a Financial Planner: This Layered Approach for Your Retirement Money Can Help Lower Your StressTo be confident about retirement, consider building a safety net by dividing assets into distinct layers and establishing a regular review process. Here's how.