Your Kids' Tax Brackets Could Lead to Unequal Inheritances
Sometimes, divvying things up equally means one child might end up with less because of tax implications. Here’s how to avoid that.


Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Today
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more delivered daily. Smart money moves start here.

Sent five days a week
Kiplinger A Step Ahead
Get practical help to make better financial decisions in your everyday life, from spending to savings on top deals.

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Closing Bell
Get today's biggest financial and investing headlines delivered to your inbox every day the U.S. stock market is open.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Adviser Intel
Financial pros across the country share best practices and fresh tactics to preserve and grow your wealth.

Delivered weekly
Kiplinger Tax Tips
Trim your federal and state tax bills with practical tax-planning and tax-cutting strategies.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Retirement Tips
Your twice-a-week guide to planning and enjoying a financially secure and richly rewarding retirement

Sent bimonthly.
Kiplinger Adviser Angle
Insights for advisers, wealth managers and other financial professionals.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Investing Weekly
Your twice-a-week roundup of promising stocks, funds, companies and industries you should consider, ones you should avoid, and why.

Sent weekly for six weeks
Kiplinger Invest for Retirement
Your step-by-step six-part series on how to invest for retirement, from devising a successful strategy to exactly which investments to choose.
Estate planning is a critical aspect of comprehensive financial planning, especially when it comes to ensuring your heirs receive the maximum benefit from your legacy. Among the various components of estate planning, the designation of beneficiaries for individual retirement accounts (IRAs) is a particularly nuanced decision with far-reaching tax implications.
The distinction between Roth IRAs and traditional IRAs (or company retirement plans) is crucial to understand when planning for the future of your heirs. Each type of account is subject to different tax rules upon distribution:
- Roth IRAs. These accounts offer tax-free distributions to beneficiaries, which can be particularly advantageous for heirs who are in higher tax brackets.
- Traditional IRAs and retirement plans. Distributions from these pre-tax accounts are taxed according to the beneficiaries' individual tax rates, which means that the actual amount received after taxes can vary significantly among your heirs.
A one-size-fits-all approach in designating equal percentages to each beneficiary may not be the most effective strategy. Instead, a more tailored approach that considers the unique tax brackets of each beneficiary can lead to a more equitable distribution of your estate.
From just $107.88 $24.99 for Kiplinger Personal Finance
Become a smarter, better informed investor. Subscribe from just $107.88 $24.99, plus get up to 4 Special Issues

Sign up for Kiplinger’s Free Newsletters
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and more - straight to your e-mail.
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice - straight to your e-mail.
Impact on after-tax inheritance
Consider a scenario where Clara is 80 years old and looking to maximize the amount that goes to her heirs, subsequently reducing the amount claimed by Uncle Sam at tax time. Ray is a prominent attorney in the highest tax bracket of 37%. Steven earns less money and falls in the 12% federal tax bracket.
Clara has $1 million in a traditional IRA (pre-tax account) and $500,000 in a Roth IRA. Initially, she had split both accounts 50/50 between her two sons. However, leaving more of the tax-free Roth to Ray may make sense because he is the higher-earning beneficiary. More of the traditional IRA could be left to Steven, as he is in a lower tax bracket, and the taxable distributions from the IRA are less impactful. Consider the following:
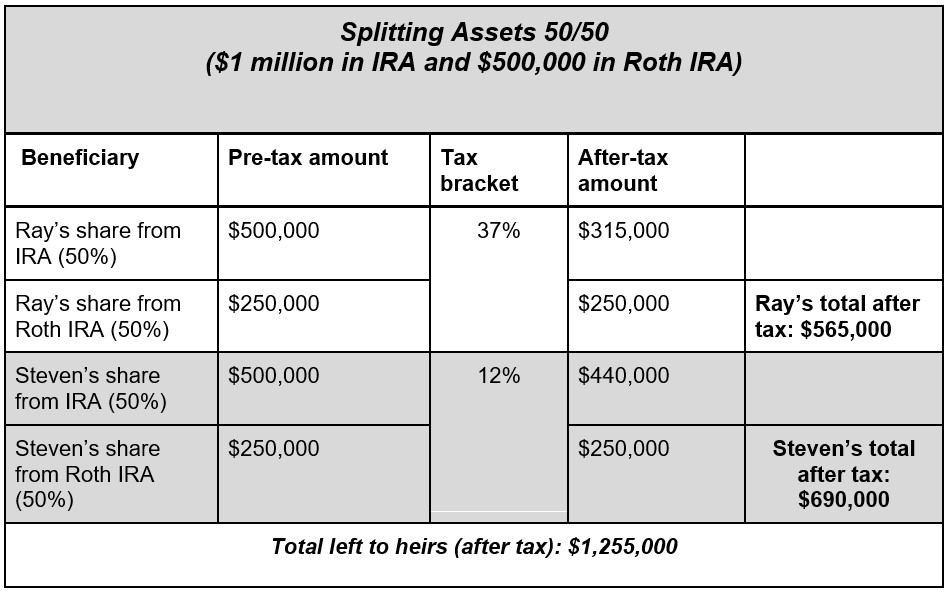
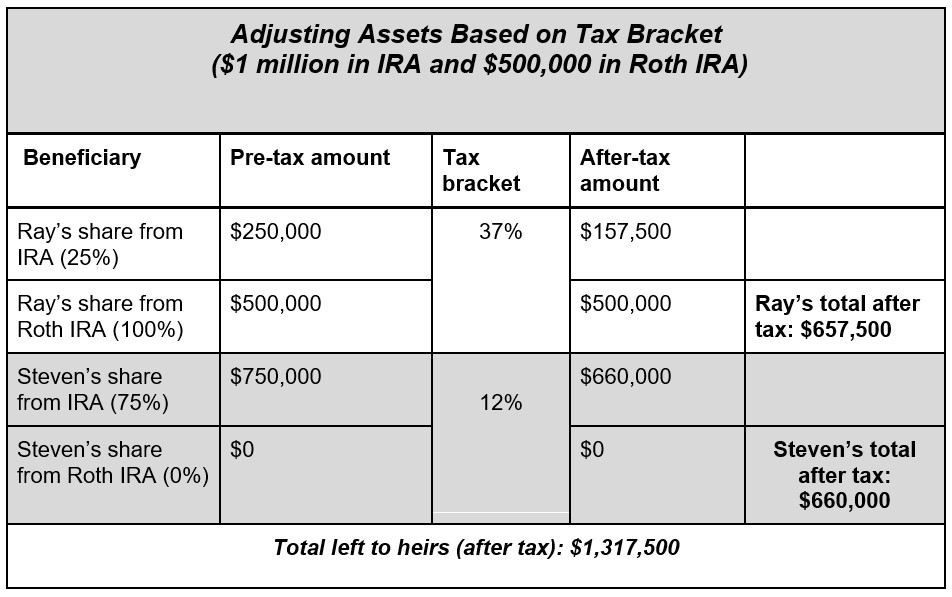
By adjusting the amount going to each beneficiary, Clara's distribution was more equitable to each child. She also was able to have less of her inheritance lost to taxes. In fact, she was able to give her heirs a total of $62,500 more ($1,317,500 - 1,255,000) than by splitting each account 50/50.
This also works when considering how much to leave a beneficiary from taxable brokerage accounts. Because of how capital gains are taxed, you may be able to leave your heirs more money by adjusting the amount each beneficiary receives based on their tax bracket.
Tax-efficient estate planning
In essence, strategically designating IRA beneficiaries transcends mere asset distribution; it is a testament to the power of informed financial planning and the profound impact of tax considerations on inheritance. This example illuminates a path for families that can significantly enhance the value of their legacy for their heirs.
By eschewing the traditional equal-split approach in favor of a model that aligns with each beneficiary's unique tax situation, individuals can ensure that their heirs are positioned to receive the maximum possible benefit from their inheritance. This method not only honors the benefactor's intent to provide for their loved ones but does so in a manner that is both tax-efficient and equitable, allowing for a legacy that is felt more deeply and preserved more completely.
The case of Clara and her sons serves as a compelling illustration of how adjusting beneficiary designations to account for different income levels and associated tax brackets can result in a more favorable after-tax outcome. Such strategic adjustments, while requiring careful consideration and possibly the guidance of a certified financial planner, can significantly reduce the tax burden on the estate. This allows a greater portion of one's life savings to reach the intended recipients — fully embodying the true spirit of a given legacy.
Investment advisory services offered through Osaic Advisory Services, LLC (Osaic Advisory), a registered investment advisor. Osaic Advisory is separately owned and other entities and/or marketing names, products or services referenced here are independent of Osaic Advisory.
Related Content
- Resist the Taboo: Talk to Your Kids About Family Wealth
- To Protect Your Kids, Consider These Estate Planning Steps
- Four Ways to Give Money Tax-Free to Your Kids When You Die
- IRS Quietly Changed the Rules on Your Children’s Inheritance
- How to Optimize Taxes When You Tap Your Retirement Accounts
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.

Antwone Harris, MBA, CFP®, is a seasoned financial professional with over 20 years of experience helping clients transition from their main careers to the next phase of their lives. As a former VP-Senior Financial Consultant at Charles Schwab Inc., he managed over $890 million in client assets and ranked in the top 5% of more than 1,100 advisers nationwide. His financial expertise has been featured in major media outlets such as CBS, ABC, NBC, FOX, The Washington Post, Bloomberg, The Financial Times and Kiplinger. Harris is a CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER™ and a Retirement Income Certified Professional®, focusing his practice on creating comprehensive plans for individuals approaching or already in retirement. Recognizing the anxiety surrounding retirement preparation, Harris founded Platinum Bridge Wealth Strategies to provide specialized financial planning for those nearing or in retirement.
-
 5 Vince Lombardi Quotes Retirees Should Live By
5 Vince Lombardi Quotes Retirees Should Live ByThe iconic football coach's philosophy can help retirees win at the game of life.
-
 The $200,000 Olympic 'Pension' is a Retirement Game-Changer for Team USA
The $200,000 Olympic 'Pension' is a Retirement Game-Changer for Team USAThe donation by financier Ross Stevens is meant to be a "retirement program" for Team USA Olympic and Paralympic athletes.
-
 10 Cheapest Places to Live in Colorado
10 Cheapest Places to Live in ColoradoProperty Tax Looking for a cozy cabin near the slopes? These Colorado counties combine reasonable house prices with the state's lowest property tax bills.
-
 Don't Bury Your Kids in Taxes: How to Position Your Investments to Help Create More Wealth for Them
Don't Bury Your Kids in Taxes: How to Position Your Investments to Help Create More Wealth for ThemTo minimize your heirs' tax burden, focus on aligning your investment account types and assets with your estate plan, and pay attention to the impact of RMDs.
-
 Are You 'Too Old' to Benefit From an Annuity?
Are You 'Too Old' to Benefit From an Annuity?Probably not, even if you're in your 70s or 80s, but it depends on your circumstances and the kind of annuity you're considering.
-
 In Your 50s and Seeing Retirement in the Distance? What You Do Now Can Make a Significant Impact
In Your 50s and Seeing Retirement in the Distance? What You Do Now Can Make a Significant ImpactThis is the perfect time to assess whether your retirement planning is on track and determine what steps you need to take if it's not.
-
 Your Retirement Isn't Set in Stone, But It Can Be a Work of Art
Your Retirement Isn't Set in Stone, But It Can Be a Work of ArtSetting and forgetting your retirement plan will make it hard to cope with life's challenges. Instead, consider redrawing and refining your plan as you go.
-
 The Bear Market Protocol: 3 Strategies to Consider in a Down Market
The Bear Market Protocol: 3 Strategies to Consider in a Down MarketThe Bear Market Protocol: 3 Strategies for a Down Market From buying the dip to strategic Roth conversions, there are several ways to use a bear market to your advantage — once you get over the fear factor.
-
 For the 2% Club, the Guardrails Approach and the 4% Rule Do Not Work: Here's What Works Instead
For the 2% Club, the Guardrails Approach and the 4% Rule Do Not Work: Here's What Works InsteadFor retirees with a pension, traditional withdrawal rules could be too restrictive. You need a tailored income plan that is much more flexible and realistic.
-
 Retiring Next Year? Now Is the Time to Start Designing What Your Retirement Will Look Like
Retiring Next Year? Now Is the Time to Start Designing What Your Retirement Will Look LikeThis is when you should be shifting your focus from growing your portfolio to designing an income and tax strategy that aligns your resources with your purpose.
-
 I'm a Financial Planner: This Layered Approach for Your Retirement Money Can Help Lower Your Stress
I'm a Financial Planner: This Layered Approach for Your Retirement Money Can Help Lower Your StressTo be confident about retirement, consider building a safety net by dividing assets into distinct layers and establishing a regular review process. Here's how.